Sustainability in textile dyeing and finishing process aids in productive consumption of natural resources, reduction of production cost and waste generation. Basically, a sustainable development focuses on the cultural, social, economic, environmental and technological aspects of textile process and production.
Textile industries faced many challenges in dyeing and finishing. The dyeing and finishing sector includes processes like: coloration, processing, and functionalization unit in the textile industry that is high cost, energy, and harmful chemical-demanding process. Sustainability is key factor that remains as a prescription for theses various challenges posed by textile industries in managing the consumption of water, energy, harmful chemicals and so on. Textile dyeing and finishing in a sustainable method can be achieved by using chemical-free natural dyes and using kin to environment processes.
Textile Dyeing and Finishing Sector:
The dyeing and finishing sector is a fundamental sector of textile. Dyeing is an important sector where colour or pigments are applied to the yarn or fabric. Colour is known as a pigment which is strongly shaded in the fabric with the help of a mordant. Mordant is a chemical which strongly holds the pigments or colour to the fabric even after washing or usage.
Types of dyeing methods:
- Natural dyeing
- Synthetic dyeing
- Industrial dyeing
- Tie dyeing
- Dip dyeing
- Batik
- Resist dyeing
- Shibori
- Tritik
You may also like: Different Types of Dyeing Methods
Textile finishing is the processing of fabric through various mechanical and chemical finishing methods which enhances the quality of the fabric. It is one of the preparatory techniques used prior to various processes such as dyeing, sizing and manufacturing. The finishing process aids in providing the functional properties such as flame resistance, water resistance and wrinkle resistance to the fibre, fabric or cloth which enhances the quality of the clothes and its longevity.
Types of textile finishing methods:
- Mechanical finishing.
- Chemical finishing.
- Enzymatic finishing,
Sustainability in Textile Dyeing and Finishing:
The world population will be increased around 35 percent by 2050. As a result, the consumption of textiles will be increased. The increase in textile consumption will increase the use of water and energy, as well as the chemicals and total discharged wastes in the textile industry.
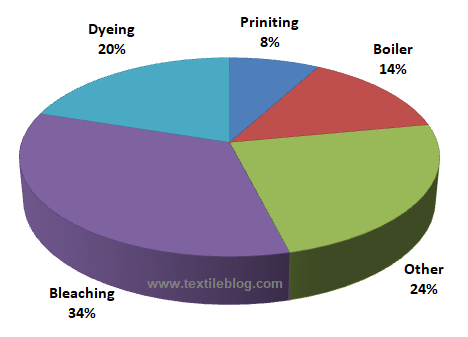
As we know the textile industry is one of the largest contributors to environmental threats globally. Cause its producing 60 billion kilograms of fabric annually and using up to 9 trillion gallons of water in textile dying and printing process. Evaluate the sustainable dyeing and finishing methods like: plasma, ultrasonic, laser, and supercritical carbon dioxide dyeing, which can enrich specific properties of fabrics without causing adverse effects on the environment.
Detailed information about the environmentally friendly sustainable methods in textile dyeing and finishing discussed as follow:
1. Sustainable dying process using natural ingredients:
Sustainable application of Natural Dyes:
Natural dyes are obtained from various natural sources like: vegetables, minerals, and animals. The production and uses of synthetic dyes has involved many chemical reactions with petrochemical-based dye intermediates. Thats are high energy consuming and deliver hazardous toxic chemicals to our environments. For this pollution problem of synthetic dyes had led many researchers worldwide to reinvestigate the methods of producing eco-friendly natural dyes textile products for future eco-textiles.
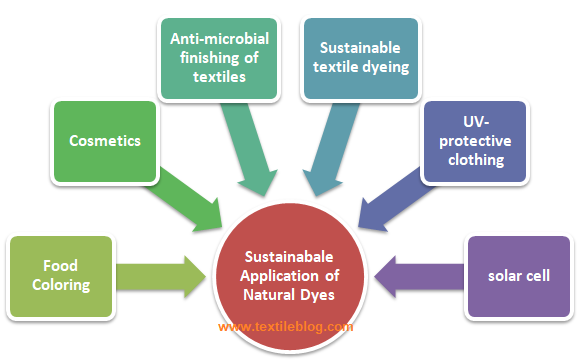
Vegetables offer plenty of colour choice; as a result it’s used widely. It had been used to colour leather, textile materials, and other crafted products for more than 1000 years. Most natural dyes are cultivated such as: turmeric, onion leaves, marigold, annatto, indigo and so on. Sustainable application of Natural Dyes is becoming popular for its advantages.
The advantages of natural dyes:
- Production of soft, lustrous colours
- Availability of a wide range of colours
- Production of rare colours
- Non-reproducible shade
- Extraction from renewable sources
- Durability and fastness properties
- Nonhazardous nature
- Ease of disposal
- Lack of environmental threats
- Reduced carbon emissions
- Biodegradability
- Eco-friendliness
Popular natural dyes:
- Turmeric: Turmeric dye is a bright yellow powder which is extracted from the rhizomes of Curcuma longa. It is a natural substantivity dye. Therefore, it can be applied to cotton and other natural fibres without the need for any other chemicals
- Tea: Tea is one of the most widely consumed beverages that chemically contains various compounds such as caffeine, polyphones, fluoride, amino acids, and organic acids. The colours of different teas depend on the degrees of fermentation and oxidation of the polyphones. Teas provides into six colours: black, dark, green, oolong, white, and yellow.
- Henna: Humans have used henna to make colourful design on the hands and feet for thousands of years. It had also been used to draw paintings on walls and to colour textiles with or without the use of a mordant. Henna can be used to colour nylon 6.6, silk, and wool. Henna could helps postmordanting to improve the washing and light fastness of textiles.
2. Sustainable finishing process using natural ingredients:
Sustainable application of natural finishing:
Textile finishing is an important process for improving the value of the textile products. Many finishing processes involve hazard chemicals. Today, due to increasing awareness of the global warming issue, the use of the sustainable finishing processes with natural ingredients is increasing in every stage of textile processing.
Anti-microbial Finish by natural ingredients:
- Papaya (Seed and Leaf)
- Aloe Vera
- Neem
- Banana (Leaf and Peel)
- Mango
- Pomegranate
- Combinations of Various Sources:
- Pomegranate + Onion
- Neem + Aloe Vera
- Tulsi + Turmeric + Neem
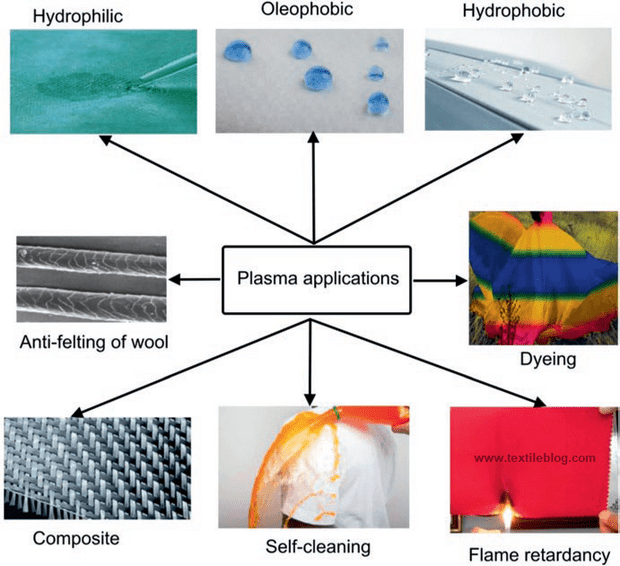
3. Plasma processing for dyeing and finishing:
Surface modification of textile materials needs to create a reactive surface suitable for dyeing and finishing treatments. Plasma technology is the techniques used by the textile industry to enhance some of the properties such as strength, hydro-phobicity and hydro-philicity, antistatic properties, adhesion properties, functionalized fibre, dyeing and printing ability of the fabrics, and so on. It is applied to textile fabrics to modify the surface, which helps to enhance the functional properties. These technologies reduce the consumption of energy and other resources during the textile dyeing and finishing process. Plasma technology is one of the most innovative and sustainable technologies found in the textile industry
Plasma applications and their effects on substrates:
| Process | Nature of process | Effects obtained |
| 1. Alteration of surface energy |
| Wettability, printability, dyeability, wickability, functional applications, washability. |
| 2. Alteration of cohesive properties |
| Cross-linking of polymers, handle modification, washability. |
| 3. Alteration of adhesive properties |
| Painting of surfaces without volatile organic chemicals, composite structures, medical applications. |
| 4. Alteration of electrical characteristics |
| Antistatic finish, charging and discharging action in photocopying, breathing masks, charge embedding in non-wovens, filtration. |
| 5. Alteration of surface finish |
| Adhesion of liquids, etching, scratch resistance, altering optical characteristics.
|
| 6. Altering bulk properties |
| Modification of tensile and compressive strength, elasticity, density. |
| 7. Removal of microorganism |
| Sterilization, disinfection, cleaning and antisepsis. |
Plasma used to create various functional textile materials shown in the below figure.
4. Bio-mordants:
A mordant is a metallic compound which helps to make a bond between a natural dye and a fabric, resulting in better fastness properties. Although some natural dyes like: turmeric does not require a mordant since it have good substantivity properties. But, the majority of natural dyes does not have good substantivity. That’s why, utilization of a mordant is important. The safest mordants to use are alum and ferrous sulphate. The examples of toxic mordants are copper and chrome-based mordants. Therefore, uses of bio-mordants could be an alternative to use of toxic metallic mordants. Cause of its potential for sustainable use.
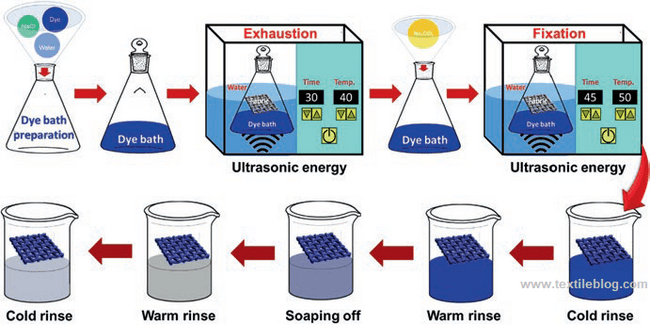
5. Ultrasound-assisted dyeing and finishing:
Ultrasound was first used in textile industry commercially in 1917. The frequency of ultrasonic energy is between 20 kHz to 500 MHz. For sustainable dyeing and finishing, ultrasonic energy utilizes to perform the coloration process with the least formation of pollutants. The ultrasonic energy can create cavitations in the liquid phase, modifying the surface properties of the treated textile materials.
6. Solvent dyeing:
Dyeing is an important process in the textile industry where it consumes a large amount of water. Besides, the effluent released from the dyeing unit is composed of toxic chemicals, dyes, pigments, salts, acids, many organic and metallic compounds. In order to overcome all these negative effects of dye-polluted wastewater, textile production with sustainable approaches are mandatory. Solvent dyeing is considered as the sustainable techniques that can reduce the severity of the dyes and pigments.
In solvent dyeing technique, dyes are dissolved using solvents instead of water. As a result in enhanced adsorption of dyes onto fabrics. Supercritical carbon dioxide can be used as solvents in this technique. It is highly effective in dissolving the dyes because of its peculiar characteristics like: low viscosity and high density. It also serves as an efficient medium for dyeing the fibres.
7. Zero discharge dyeing:
The wastewater released from the dyeing unit is always remains as one of the biggest problems in the textile industry. Zero discharge dyeing is a effective methods to stabilize lack of water by effective utilization of the spent textile wastewater.
This zero discharge dyeing method reduces the risk of textile effluents getting discharged into environmental. For reusing the effluent, the wastewater released from the textile dyeing unit is subjected to jigger. Then it is processed for the next batch of dyeing. This method is very profitable, effective, consumes less energy and water which satisfies the conditions of sustainability.
8. Sustainable flame retardants:
Flame retardants are one of the most important functional finishing systems. Several compounds like: di-ammonium phosphate, urea, melamine-formaldehyde, THPC, antimony-halogen, and phosphorus found in the traditional flame retardants. But they are found to be toxic and have deleterious effects on the environment.
In these situations, the utilization of caseins, nucleic acid, DNA, proteins and hydro-phobins is considered as great alternatives for the traditional finishing materials. These materials help in the production of flame retardants fabrics with enhanced thermal stability
9. Sustainable UV technology:
Ultra-Violate exposure at low concentrations helps in killing the pathogens and others disease causing microbes. But UV radiation it causes wrinkles, skin damage, blisters, ageing, and so on in the skin layer. That’s why UV protective clothing has gained attention in textile industry. In order to overcome these harmful effects, UV protective finishing is implemented in the fabric. For the synthesis of UV protective clothing, several natural sources extracted from mulberry, grapes, tulsi, aloe vera, honey, almonds, etc, are utilized in UV-resistant fabrics to enhance sun protection.
10. Implementation of nanotechnology:
Nanotechnology is one of the sustainable technologies in the textile dyeing and finishing sector. This technology uses textile fibres on a nano-scale, a diameter range of about 1–100 nm. The implementation of nanotechnology in the textile has already proved a positive impact on the enhancement of the surface area of the separate fibres. The sustainable implementation of nanotechnology in the textile industry can reduce the usage of harmful and toxic chemicals which damage the environment.
Conclusion:
Traditional dyeing and finishing methods influence the environment in a negative way. That’s why, the necessity for sustainable approaches is increasing day by day. Some of the sustainable approaches like: plasma technology, nanotechnology, UV technology are implemented in the textile industry for the betterment of our environment. As a result, sustainable dyeing and finishing processes in the textile industry have earned a lot of attention, for the emerging concept of sustainability.
References:
- Sustainability in the Textile and Apparel Industries: Production Process Sustainability by Subramanian Senthilkannan Muthu and Miguel Angel Gardetti https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/7250/eco-textile-dyeing-and-finishing
- https://www.prescouter.com/2018/11/sustainable-dyeing-innovations-greener-ways-color-textiles/
- https://www.lead-innovation.com/english-blog/sustainable-solutions-in-the-textile-industry
- https://www.intechopen.com/online-first/bio-dyes-bio-mordants-and-bio-finishes-scientific-analysis-for-their-application-on-textiles
Author of this Article:
Md. Mahedi Hasan
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali.
Email: mh18.bd@gmail.com
