What is a V-bed Knitting Machine?
V-bed knitting machine is a widely used knitting machine. There are two types of knitting machine; one is V-bed rib machine and other is flat bed purl machine. V-bed machine have two rib gated, diagonally approaching needle beds. Flat bed purl machines have horizontal needle beds. Both they used double headed latch needle that are transferred to knit in either of two directly opposed needle beds. Lots of knitted products like half cardigan, full cardigan are produced by v-bed knitting machine. Even seamless garments can be produced from here.
V-bed or flat bed knitting machine consists of 2 flat needle beds arranged in an upside-down “V” formation. These needle beds can be up to 2.5 meters (8 ft. 2 in) wide. A carriage, also known as a Cambox or Head, moves backwards and forwards across these needle beds, working the needles to selectively, knit, tuck or transfer stitches. A flat knitting machine is very flexible, allowing complex stitch designs, shaped knitting and precise width adjustment. It is, however, relatively slow when compared to a circular machine. Knitting speed up to 0.5 meters per second (1.6 ft./s) or slower is considered the low speed in flat knitting which are generally in hand flat machines.
Objects:
- To acquire the knowledge of identification about the main parts of the V-bed knitting machine.
- To know about the cam arrangement of the machine.
- To acquire the knowledge of their functions and uses.
Specification of V-bed Knitting Machine:
- Name: V-bed knitting machine
- Machine length: 32 inch
- Machine gauge: 12
- No of feeder: 4
- Knit cam: 2
- Tuck cam: 2
- Stitch cam: 2
- Company name: Leading tiger
- Origin: China
Different Parts of V-bed Knitting Machine:
- Yarn guide
- Yarn carrier
- Yarn package
- Tension spring
- Cymbal tension
- Yarn take-up
- Fabric comb
- Back needle bed
- Front needle bed
- Needle spring
- Fabric
- Dead weighting system
- Latch needle
Yarn to Fabric Path Diagram of V-bed Knitting Machine:
The following Figure 1 shows a cross section of a simple hand powered and multiplied V-bed rib flat machine. The trick walls are replaced at the needle bed verges by thinner, polished and specially shaped knock-over bit edges.
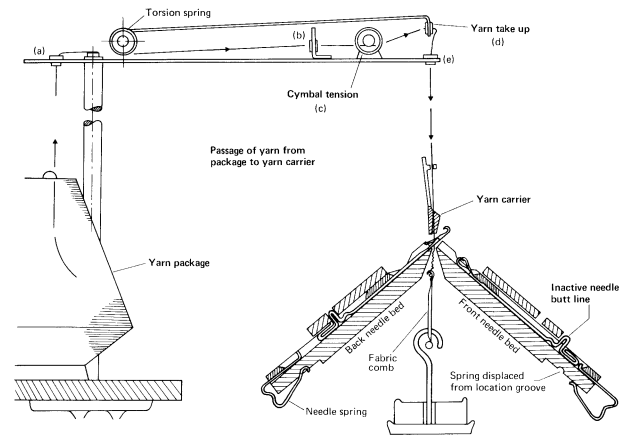
In the Figure 1, yarn goes from the yarn package through the yarn take up to yarn carrier. From the yarn carrier yarn goes to the latch needles which perform knitting action through traversing motion by the help of cam arrangement. There is a tension spring and cymbal tension device in the knitting action of V-bed knitting machine. By the knitting action loops is formed and fabric is made.
Cam Arrangement of V-bed Knitting Machine:
The single knitting system cam box is symmetrically designed for knitting a course of loops on both the front bed and back bed needles during a right to left traverse and a second course during the return left to right cam box traverse.
The needles butts will enter the traversing cam system from the right during a left to right carriage traverse and from the left during a right to left traverse. For each needle bed there are raising cams, two stitches and one guard cam. (The cam arrangement is shown in the Figure 2).
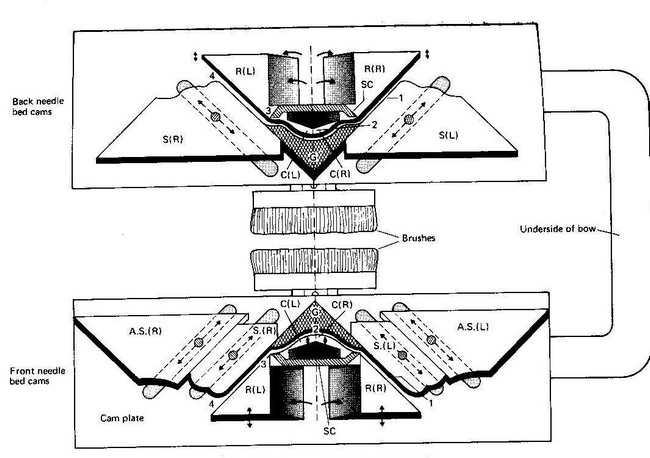
Raising cam:
In a cam arrangement two raising cams are placed side by side. They are placed at the bottom, arising cam lift the needle to tuck height. A raising cam has three different heights that help needle to form different loops.
- Full height
- Half height
- No height
Tuck cam:
Like raising cams two tuck cams are placed side by side. They are placed upon the raising cams. A tuck cam helps needles to form various design loops. Like raising cam it has also 3 different heights that help needle to form different design loops.
Guard cam:
There is one guard cam in a cam arrangement. Guard cam is placed above the two tuck cams. A guard cam controls the rising of needles. This cam is a fixed in position.
Stitch cam:
There are two stitch cams in a cam box. They are placed at the two sides of the previous three cam arrangement. A stitch cam has also three positions that control the GSM of the fabric.
Knitting Action of V-bed Knitting Machine:
The knitting action of V-bed machine has four steps. These steps are illustrated below with Figure 3.
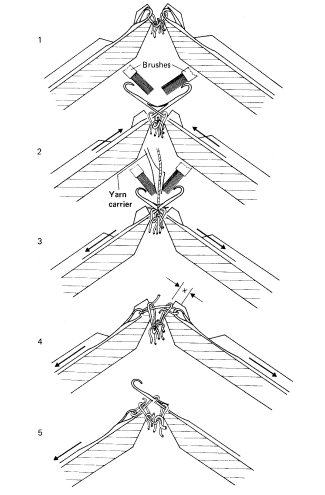
1. The rest position:
The tops of the heads of the needles are level with the age of the knock over bits. The butts of the needle assume a straight line until contacting the raising cam leading stitch cams are lifted to an inactive position. The lifting action is an alternating action that always lowers the trailing stitch cams and raises the leading stitch cams in each system as the traverse commences. This action prevents needles from being unnecessarily lowered and a strain being placed on the old loops prior to the start up of the knitting action.
2. Clearing position:
The needle butts are lifted as the y contact the leading edge of cams that raise the needle to “tucking in the hook” height with the under surface of cams acting as guard cams. The needles are lifted to full clearing height as their butts pass over the top of the tuck cams.
3. Yarn feeding:
The yarn is fed as the needles descend under the control of guard cam. Each needle draws the required loop length as it descends the stitch cam.
4. Knocking over:
To produce synchronize knocking over of both needle bed simultaneously; the stitch cam front system is set lower the auxiliary stitch cam so that the later is rendered ineffectively. If, however delayed timing of knock over is employed, knock over in front bed will occur after knock over in the back bed. In this case, stitch cam is not set as low as fig-5 so that the depth setting of the later cam produce the knock over action. Delayed timing is only normally used on gauges finer than 8npi and cannot be used for broad ribs.
Conclusion:
V-bed knitting machine is widely used in Bangladesh, India and Sri Lanka. This knitting machine can easily be operated and can yield versatile products. This experiment has significance in our study life. In this experiment we sketch the yarn path diagram of the machine, show the knitting action, cam system. We point out the various specification of the machine. So the experiment helps us to know more. Above all the experiment is a successful one.
You may also like:
- Electronic Interlock Circular Knitting Machine: Parts, Knitting Action & Cam System
- Difference between Single Jersey and Interlock Circular Knitting Machine
- Practical Study on Single Jersey Circular Knitting Machine
