What is Industry 4.0 or IR 4.0?
The term of Industry 4.0 is used to be defined, “A set of technology transformations in systems and product design, production and distribution and to describe the production process organization that are based on communicating technologies and devices.”
Industrial Revolution 4.0 or IR 4.0 is a combination of Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, the Internet of Things (IoT), Genetic Engineering, 3D Printing, Quantum Computing, and so on.
These Industrial Revolution is making the way for transformative changes in the way we live. In this blog, we’re going to break down the basics and demystify the term so you can participate in Industry 4.0
Behind the Buzzword of Fourth Industrial Revolution:
There is a German engineer and economist named Klaus Schwab. He is the founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum and author of a ground-breaking book called ‘The Fourth Industrial Revolution’. Klaus Schwabbehinds the buzzword- ‘Fourth Industrial Revolution or or Industry 4.0’.
Impact of Industrial Revolution on the Textile Industry:
| Industrial Revolution | Year | Transformation | Impact on Textile Industry |
| The First Industrial Revolution | 1784 |
| The first mechanical weaving loom developed in 1785 by Edmund Cartwright. Spinning and weaving mills become mechanized. It caused the end of hand wheeled production era |
| The Second Industrial Revolution | 1870 |
| The serial production was first invented in 1910 by Henry Ford as part of IR 2.0. Textile industry transformed from cottage based to industrial assembly lines and shifted from western to Asian countries. |
| The Third Industrial Revolution, | 1969 |
| Textile machineries become sophisticated and automated. China become a giant in textile sector.Western industries became bankrupts and shifted their production to Asian countries. |
| Industry Revolution 4.0 | Today |
| Textile industries are becoming more productive, more efficient, more secure, supply chain. |
After three Industrial Revolutions, as mechanical, electrical, and digital revolution, the world is witnessing the 4th industrial revolution.
Main Factors of Industry Revolution 4.0:
Five key features of Industry 4.0 are digitization.
- Speed: Time reduction to market through innovation cycles and short product development.
- Quality: Improvement of the processes and reduction of the waste through the real-time monitoring of production.
- Flexibility: Make the offer more dynamic through the mass-customization in the production phases.
- Security: Optimization of the security issues to avoid inactivity periods and cyber-attacks.
- Efficiency: Increase productivity with new technologies.
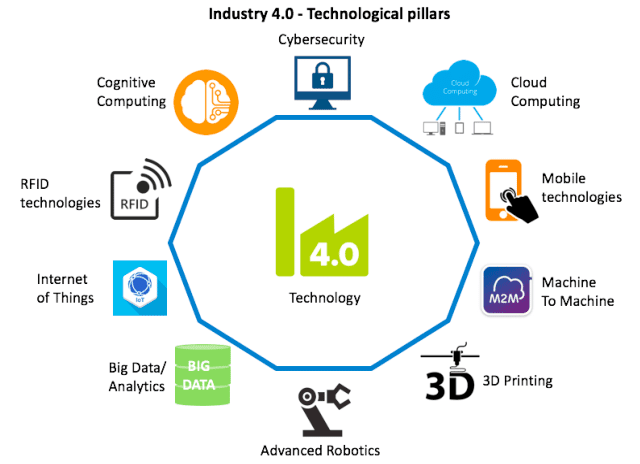
Technologies of Industry 4.0:
9 technology pillars of industry 4.0 is shown in below image:
Benefits of adopting the Industry 4.0 in Textile Industry:
- Reduced order delivery time.
- Increased quality.
- Increased productivity.
- Reduced operational costs.
- Increased customer satisfaction.
Important qualifications have to achieve for Industry 4.0:
- Knowledge about ICT.
- Ability to work with data.
- Ability to use and interact with computers & smart machines.
- Understanding machine to machine communication.
- Ability to process and analyse data and information.
- Understanding visual data output and making decisions.
- Basic statistical knowledge.
- Inter-disciplinary and generic knowledge about technology.
- Specialized knowledge about manufacturing activities and processes.
- Technical know-how of machines to carry out maintenance-related activities.
- Adaptability and ability to change.
- Decision making.
- Communication skills.
- Working in a team.
Are We Ready?
Yes. We are ready for the industrial revolution 4.0. In the situation of covid-19 corona pandemic we are all adopting the new technologies and ideas to recover. We are adopting new transformation ideas such as online shopping with zero contact, virtual office, online class, working from home, etc concept. This will be helped us to face the IR 4.0.
But important question is that, is Bangladesh will accept the of adoption of the Industry revolution 4.0?
Industry 4.0 Impacts on Bangladesh Textile Industry:
Bangladesh textile industry is still manufacturing low to mid-range ready made garments (RMG) products backed by local textile industry. Which is supplying with around 50-60 percent’s textile materials. Bangladesh still is not independent on overseas sources for sophisticated textiles including knit, woven, dyes-chemicals, accessories etc.
Demand of consumer apparels of low to mid-range products and high due to the fast fashion trends all over the world. Bangladesh is becoming an unprecedented player due to its large capacity and lower costs.
In this case, the dynamics of the global apparel market will push the Bangladesh Textile industry further to grow big in volume in the upcoming years.
Textile factories of Bangladesh will be benefited by the adopting of Industry revolution 4.0. These are:
- Shorten time and cost to market by at least 20%.
- Increase productivity and efficiency.
- Seamless information flow across the value chain.
- Enhance value addition by 10%.
- Reduce cost by 5% every year.
- Reduce rejection rate by 50% due to better control on quality.
- Initiate experiments with technology.
- Upgrade the present IT infrastructure and technology platforms.
- Shift towards compliant and environment-friendly manufacturing.
- Create sustainable advantages in business leveraging the technology.
- Re-train the work force with required skill sets for new technologies.
- Become globally competitive.
Textile Industries of Bangladesh can adopt two production models to be benefited Industry 4.0:
- Mini Factory: The most important components of Industry Revolution 4.0 are smart factories, e-production applications and interaction between smart systems for excellent production processes.
- Smart Factory: A smart factory is a highly digitized and connected production facility that relies on smart manufacturing. The concept of the smart factory is considered to be the most important outcome of the fourth IR 4.0 will boost these models to thrive.
Difficult challenges to face for adopting Industry 4.0:
1. Initial investment cost:
Cyber systems, robotics, virtual reality (VR), 3D product design, wireless sensor networks, data infrastructures and their integrations are very costly.
2. Privacy and security:
The privacy and security of digital data is an important issue for every industrial organizations.
3. Technical Challenges:
Textile Industry have to relatively face new technological. As a result, the shortage of experienced workers in these technologies is a serious constraint.
4. Lack of a global standard:
The lack of global standard developed for IR 4.0 causes another difficulty.
5. Social difficulties:
Number of required low-skilled labour force to shift towards more high-skilled complex jobs. Which requires more intense focus on emerging technologies. This brings important social problem like unemployment.
Skill related challenges with industry 4.0:
1. Up-skilling:
Companies needs to up-skill their workforce via in-house or external training centres.
2. Re-skilling:
IR 4.0 is expected to result in many job displacements to a certain extent. Companies should have to make the investment in the re-skilling of the labour force to prepare for this expected shift.
3. Continuous learning:
Technologies will become obsolete at a faster rate. Continuous professional development strategies needs to adapt the changes of technological advancement.
4. Mindset change:
Labour force will have to adapt to a number of changes, they will resist and oppose the implementation of newer technologies. Companies have to plan for mindset change of its employees to facilitate a transformation.
Conclusion:
Industry Revolution 4.0 is consisting of the innovative approaches in Textile sector. It has many benefits and challenges of Apparel 4.0 have been analyzed.
But according to Anir Chowdhury, Policy Adviser of the a2i project, “Garments will the worst sufferer of Industry 4.0 revolution as there is a possibility of 27 lakh or 60% of jobs being lost”.
Therefore, the existence of Industry 4.0 with the Bangladesh Textile Industry’s establishment level has not yet been proved in Bangladesh.
References:
- Choudhury, A.R. Environmental impacts of the textile industry and its assessment through life cycle assessment.
- Bullon, J.; González Arrieta, A.; Hernández Encinas, A.; Queiruga Dios, A. Manufacturing processes in the textile industry.
- Brettel, M.; Friederichsen, N.; Keller, M.; Rosenberg, M. How virtualization, decentralization and network building change the manufacturing landscape: An industry 4.0 perspective. Int. J. Mech
- Rüßmann, M.; Lorenz, M.; Gerbert, P.; Waldner, M.; Justus, J.; Engel, P.; Harnisch, M. Industry 4.0: The Future of Productivity and Growth in Manufacturing Industries
- Lee, J.; Kao, H.-A.; Yang, S. Service innovation and smart analytics for industry 4.0 and big data environment.Procedia Cirp 2014, 16, 3–8
- https://textilelearner.net/industry-4-0-for-textile-and-apparel-industry/
- https://www.dhakatribune.com/business/2018/02/01/ready-industry-4-0
- http://textilefocus.com/bangladesh-textile-apparel-industry-industry-4-0/
- https://www.textiletoday.com.bd/introducing-industry-4-0-bangladesh/
- https://www.thedailystar.net/opinion/economics/news/bangladeshs-apparel-sector-ready-industry-40-1742011
Author of this Article:
Md Mahedi Hasan
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali.
Email: mh18.bd@gmail.com
