Analysis of Cut Panel Inspection of a Knit Composite Factory
Authors:
Md. Ibrahim Khalilullah1
Md. Al-Kamran
Dept. of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University, Dhaka
Email: ibrahimdiutex22@gmail.com1
Abstract
Cutting is the most need arranges in labor escalated instant garments undertakings. Quality Faults happening amid this procedure antagonistically influence the item quality and item effectiveness, and furthermore increment the creation cost. The point of this examination is to research whether the knitwear creation process is under control in a knitwear generation venture and to identify the procedures with most noteworthy rates of cutting issues in sewing office lastly to make recommendations for enhancing the quality control. We did this work by collecting enough data and information from a factory. Then we analyze it depends on the data. We try to find out the percentage of different fabric faults and make a chart of the fault percentage. We make a list of faults from higher to lower fault. Here, we also make sure the efficiency of cutting. As a result, we found 2.92% fabrics are faulty where Fabric hole(%), spot(%) Dyeing fault (%) slub(%), knot(%) yarn fault(%). It’s a little amount of fault from the total amount which can consider for the next process. In addition, this study is help us to know all about the cutting fault and how we can reduce the fault, daily production and cutting control. Cut panel inspection is done to identify any types of fabric defect if any defective panel found or if there any discrepancy, a correction will be immediate.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background of the Project
The business of Ready Made Garments in Bangladesh started in the late 70s with just non-formal effort. The very first consignment of knitwear export was generated in 1973, whereas the primary shipment of knitwear was made in 1977. In 1981-82 thecontribution of apparel or RMG to total exports was regarding 1.10% whereas theagriculture-based economy received a lot of foreign earnings from Jute. Jute called as the Golden Fiber. However, by passing the time from agricultural to producing transformation Bangladesh developed significantly in areas of economic condition alleviation, employment, women empowerment, industrial growth and economic variegation–special gratitude tolabor intensive RMG sector. Though MFA terminate in 2004, the expansion of Bangladesh knitwear has improved very fast despite its somewhat littered and shoddy begin with absence of rudimentary plans and organic process industrial mechanism. In fact, from year 2007-08 Bangladesh knitwear achieving to capture lion’s share in national exports (39.93% in FY 2013-14) what was slightly 7.64% within the 20 years back, thereby diagonal the economy towards knit garments.
1.2 Objectives of the Project
Every company tries to express their value to their customers with their highest quality products. So, Quality control is the most effective way to produce the high standard quality product. Quality control is the most absolute approach to create the elevated expectation quality item for customer or buyer. The main aspiration of Quality control is the satisfaction of consumer needs and wants to keep the item popular and eco-friendly.
The major objectives of this study were as follows:
- To identify different types of cutting faults.
- To identify major problems in cutting.
- To identify the causes and remedies of the problems in cutting.
- To analyze cut panel inspection.
- Percentage of defect and total ok quality identifying.
1.3 Limitations of the Project
The main limitations of the project are as follows:
- Due to time deficiency we couldn’t get valuable information of the quality controller operation. We couldn’t get enough data because quality controller always busy with his work.
- We couldn’t collect sufficient records and recent statistical data from the QC. So, this limitation limited the extent of the genuine analysis.
- There is no research-oriented room.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Introduction
Quality denotes an excellence in goods and services, especially to the degree they conform to requirements and satisfy customers.
Quality control of garments cutting section plays an important role in garments because right measured cutting is needed to get the correct form of garments product. Cutting is that the first operating department of garments production. Before making a cloth, you have to cut of individual elements as per approved pattern, wherever as correct measuring should be ensured so all cutting elements should be 100% accurate.
2.2 Parts of Quality Control in Garments
Quality control of cutting section mainly divided into four parts. Those are:
- Marker Inspection
- Spreading Control
- Cutting Quality control
- Piece Goods Inspection
2.2.1 In Marker Inspection following things are inspected
- Marker Length
- Marker width
- Lay quantity
- Style/Lot
- Ratio
- Measure of all individual parts marked in marker
2.2.2 Following work in spreading quality control
- Cut numbers
- Ends
- Leaning
- Tension
- Narrow Goods
- Remnants
- Counts
- Ply Height
- Fabric Fault
2.2.3 Piece goods inspection
- Yarn Fault
- Hole
- Slab
- Spot Dyeing fault
- Knot
- Crease Mark
2.3 Cutting Quality Control & Flow Sequence
- Number of parts
- Miss cut
- Ragged cutting
- Notches
- Matching plies
Flow Sequences of Cutting:
Fabric Inspection
↓
Fabric sends to store
↓
Fabric received from store
↓
Marker making
↓
Fabric spreading
↓
Setting marker on the fabric lay
↓
Fabric cutting
↓
Numbering
↓
Prepare the bundling card
↓
Bundling
↓
Quality inspection & front part- back part is fold together
↓
Send to sewing section
2.3.1 QA checkpoint during fabric layering:
- Before planning fabric layer on cutting table for cutting a specific style, QA individual should check material swatch card, shading shade band deliberately what’s more, gather unique example to check all piece of article of clothing’s thing in marker paper.
- Should be checked cut amount/estimate group/nation astute request separate. QA can’t affirm any fragmented cutting amount.
- Precisely registration amount, texture thing, shading name, ticket number and so forth on the table to keep any misconception. Imperfection point must check on move paper-not to be utilize – if any significant issue that is wrinkle stamp, overlap check, end roll particularly covered texture.
- On the off chance that any exceptional guideline for a similar style particularly sizes proportion, must check the marker with hard example. Additionally, check two-way and one-route marker before begin layering.
- To affirm shading shade, shading, thing name, thing face-back, shrinkage rate, move width, marker width, and style class before begin layering. Above checkpoint needs to take after 100% for guaranteeing smooth generation.
2.3.2 Layer examination:
While layer spreading quality reviewer needs to look at texture physically then contrast and affirmed shading card and additionally QC shade card gave by Material control office QC. On the off chance that found any error between endorsed texture swatch with mass generation texture move without a moment’s delay hold and illuminate concern’s people, for example, Cutting boss, QC and Production. After physical checking by all worry parties and considering all related QC report/archives at that point permit cutting.
2.3.3 Fabric layer review
Reviewer should check fabric ticket data deliberately before layer spreading. Amid spreading, reviewer need to investigate by 4 point framework and make a report at that point continue petitioning for record.
Face/Back:
During spreading fabric, they should guarantee amend confront side contrast and endorsement cutting shading card and additionally QC shade card. In the event that any disparity found or confounded needs to advise concern’s individual and consider until illumination by a senior dependable individual.
Cut Panel Inspection:
Generally, cut panel inspection includes recutting, color shading checking, replacing rejected panels with good and acceptable panels, stain removing etc. After cut board numbering cutting individual will give all slice board to QC. At that point QC controller will check each cut board precisely. In view of layer report or past deformity rate, manager can choose to issue floor by irregular examination or 100% physical assessment to discover imperfection thing. Amid cut board examination, on the off chance that they found any imperfection, ought to write in slice board log book to get substitution texture from the provider by submitting deformity cut board investigation report proportion. Cut panel inspection is done to detect any types of fabric fault if any defective panel found, will be replaced from lay chart wise remnants by following the shade and pattern grain line. QC’s makes cut panel inspection reject percentage report and inform to cutting In-charge.
After placing the serial number in every component of cut panel, inspection process is started from this stage. Though rolls are accepted in initial inspection still there are some defects on the roll. So quality team does sort out those defective components during cut panel inspection. QC replace the defect component from the balance fabrics, which QC kept from each roll, depends on numbering. It is mentionable that QC does record how many layers have completed from each roll to identify the fabric for replacement. The report we are following call “cut panel inspection report”.
Cut board review:
Each working day they need to make slice board review answer to dispatch concerned area, and one ace duplicate ought to be kept for record.
Cut Panel Accuracy:
During cut board investigation, controller need to check haphazardly those cut board exactness contrast and CAD Pattern/Cutting Pattern from the Top-Middle and End of each package as assessed.
To limit texture wastage, guarantee issue, completed article of clothing’s dismissal and to build generation capacity, processing plants altruism and so forth these relies upon the adequacy of production lines cutting QC group. On the off chance that you wind up satisfied by perusing this post; you can demonstrate your respects by spreading it in web based life, for example, Facebook, Twitter, and Google+ or offer it in unearth by hitting like catch. Stay tuned with us for more updates.
2.3.4 Quality controlling areas are as follows:
1. Quality control in store area:
Store area is brought together in attire industry and all the texture results in these present circumstances unit first from the provider and inspected here and kept until the point when it is disseminated to other segment. Following controlling are checked here.
- Inventory
- Fabrics
- Material
- Swatch board making
- Cleanliness
- Reporting
2. Quality control in test segment:
Tests must be checked by quality control staff before sending it to the purchaser.
Vital focuses to be checked in test segment: Regardless of whether the examples are according to purchaser’s details or not, for example, style portrayal, draw, estimation sheet, photo and so forth and workmanship must be checked with reference test or related archives gave by the purchaser. Answer to be submitted to the merchandiser and to the prevalent.
3. Quality control in cutting segment:
Quality control of pieces of clothing cutting segment assumes a fundamental part in articles of clothing since right estimated slicing is required to get the correct state of articles of clothing. Other than cutting is the main working division of pieces of clothing generation. So its quality must be checked with deliberately.
A. Patter/Marker:
Example and marker must be checked by the quality control work force check focuses are as per the following:
- Measurement
- Gradation
- Allowances
- Pattern parts missing
- Mixed parts
- Pattern shape
- Direction of example in the marker
- Pattern arrangement as for the grain line
- Poor line checking
- Marker too wide than texture width
- Notches and Drill marks discarded
- Mismatch checks and strips
- Overlapping
- Too thick line or twofold line stamping
- Invisible line stamping
- Marker inaccurately situated on the lay.
B. Spreading:
DuringFabric spreading the accompanying focuses ought to be checked:
Fabric unwinding
- Incorrect pressure of handles
- Wrong bearing of handles
- Unacceptable harms found
- Mismatching of checks and strips
- Narrow texture
Shaded Fabric
- Misalignment of handles
C. Cutting:
- During cutting the accompanying focuses ought to be checked:
- Inaccurate cutting.
- Notches-lost, too profound, calculated, excluded or wrong compose.
- Drill marks-wrong bores, excluded, calculated.
- Knife cut-article of clothing parts harmed via reckless utilization of blade.
- Frayed edges, burned or melded edges caused by a flawed blade.
- Slits opened incorrectly of overlooked.
D. Others:
- Bundling with package card
- Numbering
- Cut board checking
- Wrong measure in the package
- Fused parts checking
- Cleanliness
- Proper putting away
- Proper is suing
- Prefer test cutting at that point mass cutting
- Reporting
2.3.5 Dimensions of Quality
By Chris Akins of Trident-Consulting LLC
8 Dimensions of Quality:
The meaning of value is regularly a fervently subject. While it might appear to be natural, when we get directly down to it, “quality” is a troublesome idea to characterize with any accuracy. The most essential meaning of a quality item is one that meets the desires for the client. In any case, even this definition is too abnormal state to be viewed as satisfactory. With a specific end goal to build up a more total meaning of value, we should think about a portion of the key measurements of a quality item or administration.
1. Performance
Does the product or service do what it’s supposed to do, among its defined tolerances? Performance is commonly a supply of competition between customers and suppliers, significantly when deliverables are not adequately defined within specifications. The performance of a product often influences profitability or reputation of the end-user. As such, several contracts or specifications include damages related to inadequate performance.
2. Conformance:
Nature of conformance is the level of the nature of item really created and conveyed through the generation or administration procedure of the association according to the details or plan. At the point when the nature of an item completely fits in with the detail (plan), the nature of conformance is regarded brilliant.
3. Reliability
The item or service may have sufficient or even prevalent measurements of value, yet at the same time succumb to negative client or open recognitions. For instance, a great item may get the notoriety for being low quality in view of poor administration by establishment or field experts. In the event that the item isn’t introduced or looked after legitimately, and bombs thus, the disappointment is frequently connected with the item’s quality instead of the nature of the administration it gets.
4. Durability
Durabilityis firmly identified with guarantee. Necessities for item solidness are frequently included inside obtainment contracts and details. For example, warrior airplane obtained to work from plane carrying warships incorporate outline criteria proposed to enhance their sturdiness in the requesting maritime condition.
5. Features
Features are usually the secondary aspects of performance, the “bells and whistles” of products and services, those characteristics that supplement their basic functioning. The line separating primary performance characteristics from secondary features is often difficult to draw. What is crucial is that features involve objective and measurable attributes; objective individual needs, not prejudices, affect their translation into quality differences.
6. Serviceability
Serviceability is the speed, courtesy, competence, and ease of repair. Consumers are concerned not only about a product breaking down but also about the time before service is restored, the timeliness with which service appointments are kept, the nature of dealings with service personnel, and the frequency with which service calls or repairs fail to correct outstanding problems. In those cases where problems are not immediately resolved and complaints are filed, a company’s complaints handling procedures are also likely to affect customers’ ultimate evaluation of product and service quality.
7. Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a subjective dimension of quality. How a product looks, feels, sounds, tastes, or smells is a matter of personal judgement and a reflection of individual preference. On this dimension of quality, it may be difficult to please everyone.
8. Perceived Quality
Consumers do not always have complete information about a product or service’s attributes; indirect measures may be their only basis for comparing brands. A product’s durability for example can seldom be observed directly; it must usually be inferred from various tangible and intangible aspects of the product. In such circumstances, images, advertising, and brand names – inferences about quality rather than the reality itself – can be critical.
2.4 Factors Affecting Quality
The quality is affected by-
- Money
- Materials
- Management
- People
- Market
- Machines and Methods
1. Money:
Most important factor affecting the quality of a product is the money involved in the production itself. In the present day of tough and cut-throat competition, companies are forced to invest a lot in maintaining the quality of products.
2. Materials:
To turn out a high-quality product, the raw materials involved in production process must be of high quality.
3. Management:
Quality control and maintenance programs should have the support from top management. If the management is quality conscious rather than merely quantity conscious, organization can maintain adequate quality of products.
4. People:
People employed in production, in designing the products must have knowledge and experience in their respective areas.
5. Market:
Market for the product must exist before management emphasizes quality of the product. It is useless to talk about the quality when the market for the product is lacking. For example, there is no demand for woolen garments in the hot climates (e.g., Southern part of India).
6. Machines and Methods:
To maintain high standards of quality, companies are investing in new machines and following new procedures and methods these days.
2.5 Quality Control
Quality control is defined as “Those planned and systematic actions which provides a mean to control and measure the characteristics of a product, process or a service to established requirements.”
Quality control as per ISO:
“The operational techniques and activities that are used to satisfy quality requirements.”
The quality control system verifies and maintains desired level of quality in an existing product or service by careful planning, use of proper equipment’s and continued inspection and corrective action as required.
Quality Control means the checking, confirmation and control of the degree or review of brilliance of a characteristic or property of the materials. It is worried about the assessment of test information and its application to control of the material procedure, crude materials, moderate item with greatest economy and consumer loyalty. The operational systems and exercises are utilized to satisfy necessity of value. To control the quality proficient labor, appropriate instrument or machine and impeccable crude materials should utilize. Quality control guarantees that all piece of clothing items meets generation models and match the first example.
2.5.1 Objective of Quality Control
It is a long-standing convention of any association to offer the clients first quality stock. The reason for this control program is to help makers in meeting their exclusive requirements. The ideal objective of value control is the satisfaction of customers or purchasers desire to keep the item sought after. The others goals of value control are
- Undamaged item
- Design is indicated and progressing.
- Proper preparing for affirmed execution
- Explore the buyers require
- Increase the marketability
- Use of particular crude materials
- Increasing the creation
- Maintaining exclusive requirement of wellbeing, wellbeing and condition
- Improving the productivity
- Reducing the cost
- Use of suitable crude materials
- Study on Quality
2.5.2 What is QC Inspection
The ISO standard characterizes investigation as “movement of estimating, looking at, testing at least one qualities of an item or administration and contrasting the outcomes and indicated prerequisites with a specific end goal to set up whether similarity is accomplished for every trademark.”
QC and Inspection
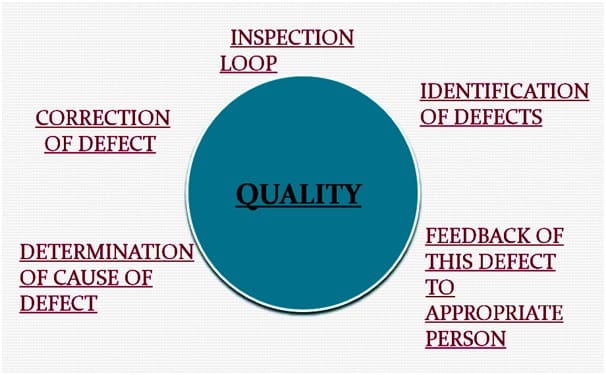
QC Throughout Production system:
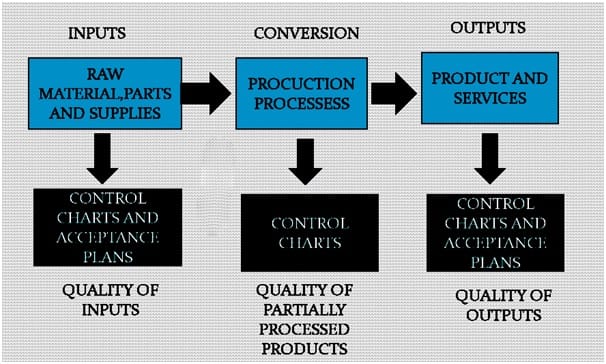
Pre- Production QC Inspection
The security and adequacy of the completed measurements shape is to a great extent reliant on the immaculateness and nature of the mass dynamic medication substance.
- Physical tests, for example, molecule estimate for crude materials stream properties and so forth are basic tests to guarantee steady task of the creation and control framework and to guarantee quality and adequacy.
- To diminish quality hazard, the data sources can be assessed preceding creation.
- Samples are arbitrarily taken and checked.
- An accomplished auditor inspects the example/model to ensure that the crude materials meet the predefined gauges.
- Whether advancement group has obviously conveyed the prerequisites to the assembling group.
- Whether supplies for large scale manufacturing is like that for making models.
IN PROCESS INSPECTION
- The main items that escaped the line are examined for similarity.
- If issues are raised at this stage, the industrial facility can quickly take activities and stay away from delays. In-process items are once in a while checked as it takes specialist to dependably distinguish mistakes on incomplete items.
IN PROCESS QC INSPECTION
- Inspect the test comes about because of in-process tests performed for conformance with built up examining and testing conventions, expository techniques, and particulars.
- For instance, assess the tests for weight variety, hardness, and friability. All testing must agree to cGMP .
- The review must affirm that the in-process tests were done, as depicted in the arrangement, and determine that the outcomes are inside details.
2.5.3 Arrangement of in process inspection
- Preliminary run examination: Tools and machines are checked before task.
- Leading examination: The things created in the main generation run are investigated and analyzed as for details.
- Review without anyone else’s input control: Done by administrators, controlling tasks at various levels of creation process.
- Decentralized investigation: Semi completed merchandise are examined either on machines or in the generation line.
- Incorporated investigation: There can be single examination unit for entire plant. Or each segment can have assessment unit to review the things. The examination staff is more experienced and talented for this situation. Sophisticated and dependable instruments and methods are use to quantify the quality. Hence unified assessment is solid and exact.
2.5.4 QC Inspection in production
- Component predominant: Incoming material must be checked for required particulars.
- Set-up predominant: An activity once set at a level, stays at that level for long. Consequently items delivered at first if discovered free from deformities and complying with determinations, at that point the task can be cleared for ceaseless activity.
- Machine predominant: Operation float away from beginning set-up level as task continues. Subsequently needs intermittent review for rectifying set up.
- Administrator prevailing: A specific segment of employment is altogether impacted by administrator’s aptitude.
- Information predominant: All the data including the SOP’s, idea of occupation is given to concerned individual.
- Record overwhelming: The composed records and documentation of each procedure and test directed ought to be kept up.
Whether advancement group has unmistakably imparted the necessities to the assembling group. Whether types of gear for large scale manufacturing is like that for making models.
2.5.5 QC Inspection in analytical
When all is said in done, these investigations include:
- The particular philosophy which will be utilized to test another medication item.
- An entire evaluation of research centers conformance with GMP’S.
- A particular part of research center tasks.
- Laboratory records and logs speak to a fundamental wellspring of data that permits an entire review of the specialized capacity of the staff and of general quality control methodology.
- SOPs ought to be finished and satisfactory and the tasks of the research centers should fit in with the composed techniques.
- Specifications and scientific methodology ought to be appropriate and, as relevant, in conformance with application duties and compendial necessities.
- Documents identifying with the detailing of the item, amalgamation of the mass medication substance, item determinations, examination of the item, and others are inspected amid the audit procedure in headquarter.
- Inspections are intended to decide whether the information submitted in an application are valid and precise and if the systems recorded in the application were really used to create the information contained in the application.
- Additionally, they are intended to affirm that plants (counting QC research facility) are in consistence with CGMP directions.
- Based on group examination approach.
- Highly specialized and concentrated testing types of gear, methods, information controls also logical research facility tasks will be assessed.
- The examination of a research center requires the utilization of perceptions of the lab in activity and of the crude lab information to assess consistence with CGMP’s.
2.5.6 FDA Inspection
FDA INSPECTION-4M’s
1. MACHINE:
- Inspection ought to affirm that preventive upkeep, cleaning, alteration and so forth are performed Machine utilization, support, alignment logs, repair records ought to be inspected.
- Verify that the types of gear were in great working request at the time the bunches were examined.
2. Technique/PROCESS:
- Data with respect to approval of strategies ought to be precisely assessed.
- All procedures that may make deviation a gadget’s detail and all approved procedure must be checked and controlled.
- On the off chance that the procedure is programming controlled, affirm that the product was approved .
- Review the product records, programming approval exercises, programming change controls and programming approval results to affirm that product will address client issue.
3. MATERIALS:
- Crude material testing is of most extreme significance as it straightforwardly influences the nature of definite item.
- Thus assessment ought to look at the investigation of materials including virtue test, quality, outlines and so on.
- Review if the strategies for breaking down the immaculateness were approved.
- The maker must have finish information of assembling process and the potential contaminations that may show up in materials.
- These polluting influences can’t be assessed by without an appropriate strategy and one that has been approved.
4. MAN:
- Check that staff have been fit the bill to execute approved procedures or fittingly prepared to actualize forms which yield comes about that can be completely confirmed.
- Affirm that the representatives have finish learning of the gadgets, forms.
- Affirm that workers know about the gadget surrenders that may happen because of disgraceful exhibitions Confirm that the representatives leading QC tests know about the deformities and blunders that might be experienced while playing out their duties.
2.5.8 Last inspection
- It is additionally known pre-shipment review.
- This is the most well known sort of QC review for merchants.
- It happens once every one of the items are done and prepared for shipment.
- The examples are attracted an arbitrary way and in this manner can be illustrative of the entire cluster.
Measurable quality control:
- It is a method for controlling nature of item utilizing an arrangement of measurable devices.
- It includes two components:
- Measurable process control: This outlines accumulation of information, makes utilization of control diagrams.
- Acknowledgment examining
Control chart:
- Main role of control outlines is to show when generation procedures may have changed adequately to influence item quality.
- In the event that the sign is that item quality has disintegrated, restorative is taken.
- Look at traits (No. of defectives in a sample) or factors (attributes that can be estimated on a ceaseless scale (weight, length, and so on.) of the example with that of the standard.
2.5.9 Sampling or sampling inspection
- It is the way toward assessing segment of the item material in a considerable measure to accept or dismissing the part as either adjusting or not complying with quality determinations.
- The acknowledgment design recognizes the:
- Size of tests,
- Kind of tests
- Choice rule, c, used to either acknowledge or dismiss the part
- Tests might be either single, twofold, or successive.
Quality audit:
- ISO characterizes review as efficient and free examination to decide if quality exercises and related outcomes agree to arranged game plans and whether these are executed adequately and are reasonable to accomplish targets.
- It checks if quality framework and techniques are Free from intrinsic imperfections.
- Are equipped for accomplishing and keeping up models of value picked by big business or costomers.
- being clung to and ordered with, in everyday work.
Quality audit and follow up:
- Prior to composing examining report, examiner discloses the perceptions to auditee. Corrective moves to be made are proposed
- Audit report are composed in standard configuration, which contain territory examined, dates of review, people reached, praiseworthy highlights and proposals.
- The report must contain status of usage of pending restorative measures according to past review.
QC inspection in distribution and storage GMP:
- Summarizes following standards as for dissemination:
- Only approved items are disseminated
- Premises are reasonable for their expected utilize and kept on great clean condition.
- All items are gotten, put away and dealt with painstakingly
- All tasks are performed by composed strategy, administered and recorded Adequate arrangement exist to deal with grievances, reviews and return products
- Storage: Warehouse ought to be perfect, blocked off for unapproved people, temperature and moistness control, satisfactory racking, free from bugs and vermin.
- Special stockpiling: Availability of chilly room/icebox for immunizations and natural items
- Special stockpiling zones for controlled medications and other doctor prescribed medications
- Suitable and secure storeroom for controlled medications and toxins
2.6 Types of Quality Control
Quality control is two types-
2.6.1 Product control
The control which is utilized to diminish deficient things inside various heaps of delivered great is known as item control. It is connected after item process.
2.6.2 Process control
Controlling of process succession or ventures to deliver wanted quality item is called process control. Process control is two composes
2.6.3 Online quality control
This kind of value control is performed in process arrange i.e. without ceasing the creation process. Checking and amendment of variety or blame in preparing stage is known as online quality control.
2.6.4 Offline quality control
This sort of value control comprises of research center tests which are finished by halting the generation process. In article of clothing fabricating typically quality faculty are designated in each area to guarantee quality yield at end of every procedure. Under every office, quality heads area QAs are delegated. In the accompanying graph, an association diagram of a medium size shirt producing organization has been appeared.
2.7 Quality Control in Cutting Section:
The Cutting section is running according to the following processes:
- Finished fabric from dyeing & finishing
- Fabric Inspection
- Relaxation
- Test of GSM, Diameter, shed, shrinkage, twisting, fastness etc.
- Test cutting
- Approval
- Marker making
- Fabric spreading
- Cutting
- Sorting (Sticker, Numbering)
- Bundling
- Cut panel inspection
- Input section
- Send to sewing section
2.8 Cutting Process:
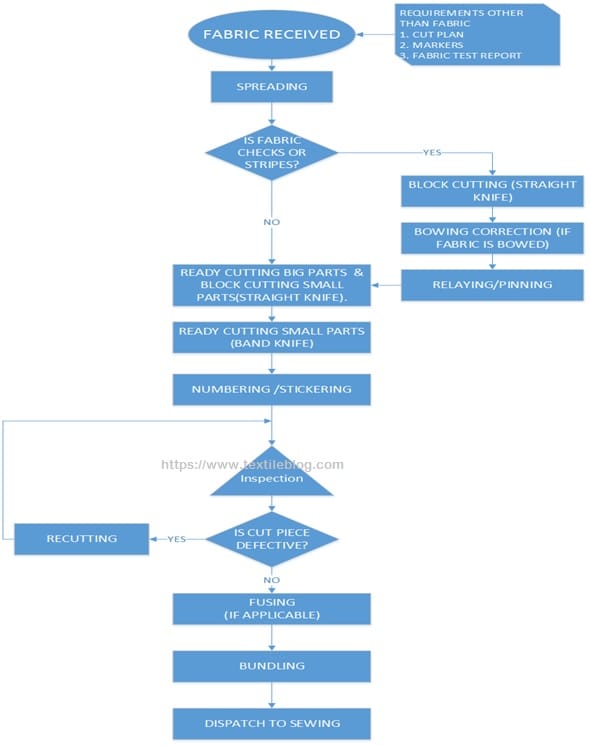
Cutting procedure in article of clothing industry can be precarious and numerous individuals are puzzled on how this mysterious accomplishment of coordinating each check/stripe is accomplished by the industrial facilities. Here is the well ordered, brief clarification on Cutting procedure in piece of clothing industry and the Cutting Process Flowchart toward the finish of the article.
2.8.1.Spreading or laying
To cut numerous articles of clothing at the same time, texture is spread in layers one over the on a long table. This procedure in called spreading or laying.
Plies: Fabric is spread in layers one over the other and each layer is known as a handle. Number of employs that can be laid is chosen in light of the tallness of the blade, thickness of texture and kind of cutting technique being taken after.
Lay: End result of spreading/laying is a lay which is only wanted number of employs laid.
Spreading should be possible by manual and additionally computerized spreaders.
Note: While spreading checks and stripes, each line of an utilize won’t cover precisely finished each other consequently if articles of clothing are cut straightforwardly line coordinating won’t be accomplished. Stick Table can be utilized as an answer for this issue.

2.8.2. Block cutting
Block cutting is improved the situation articles of clothing which requires coordinating like checks, stripes and a few prints. In this procedure as opposed to cutting straightforwardly on the examples a square is cut with cushions around the example, which takes into account coordinating the lines wherever required.
Relaying: Once a square is cut individual cut squares are handed-off superimposing the checks/stripes one over the above. The technique for handing-off can change in view of the coordinating required. Squares can be handed-off with sticking or without sticking. Goal of transferring is to superimpose checks/stripes precisely finished each other for each utilize. This is done physically.
Note: If texture is bowed, before transferring, bowing adjustment is finished by extending the texture in both predisposition bearings.
2.8.3. Ready cutting
Cutting the texture according to the state of the example is called prepared cutting. Final result of prepared cutting are the finished product parts which will be utilized for sewing. Prepared cutting is finished by various blades according to reasonableness, Type of blades can be Straight blade, Band cut and Round blade.
2.8.4. Number fixing
Cut parts are stickered or inked with numbers to recognize each piece and to ensure that each article of clothing is made in same shade and same shrinkage.
2.8.5. Panel inspection:
Cut parts are assessed by weaving surrenders. In the event that imperfections are discovered the board is supplanted by recutting a board of same shade and same shrinkage
2.8.6. Fusing
In the event that the piece of clothing contains fusible interlining the cut boards with fusible interlining are gone through combining machine which is determined to a characterized temperature to give the yield as intertwined board.
Melding is basic to quality thus uncommon care is taken to guarantee that intertwined interlining does not create absconds in later phases of item life cycle. Here and there to guarantee the right position of interlining spot intertwining is done before sending the gathering through the combining machine.
2.8.7. Packaging
After the pieces are cut, singular pieces are packaged together to be sent for sewing. In this procedure numbers are coordinated and packages are made to be sent for sewing.
2.8.8 Dispatch to sewing
You may also like: Sewing Defects Causes and Remedies in Apparel Industry
Methodology
3.1 Working Procedure
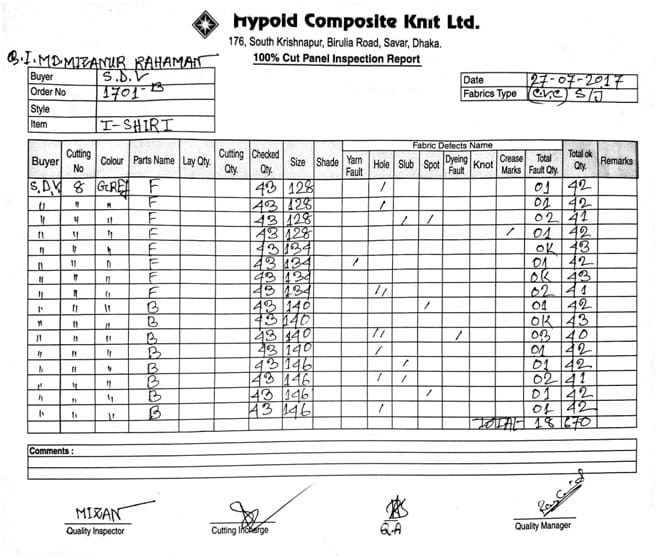
- Firstly, we havevisited the cutting section and collect 15th recent data of 100% cut panel inspection from cutting manager. But here is only shown first and last day cut panel inspection report.
- Then we identify the fault from the cut panel inspection data like yarn fault, fabric hole, slub, knot, crease mark etc. and then counts the total number of fault.
- After that, we make the total number of defects which we get from the cut panel inspection data. And get the total number of defects is 430.
- We try to mention the buyer name, order no and date exactly.
- We analyze the defect on fabric and try to collect the defect fabric sample. Then we make total defect percentage from the total okay quantity and we can understand the fault percentage which is higher and which is lower.
3.2 Inspection Data
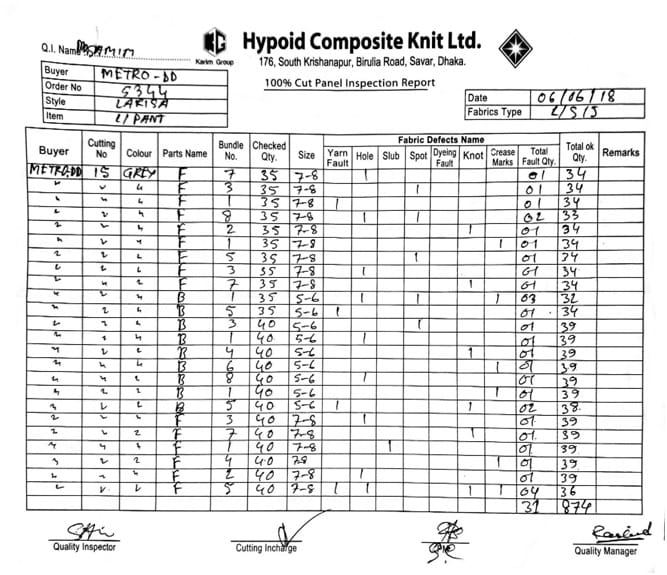
………………..
3.2.1 Summary Data
Result and Discussion
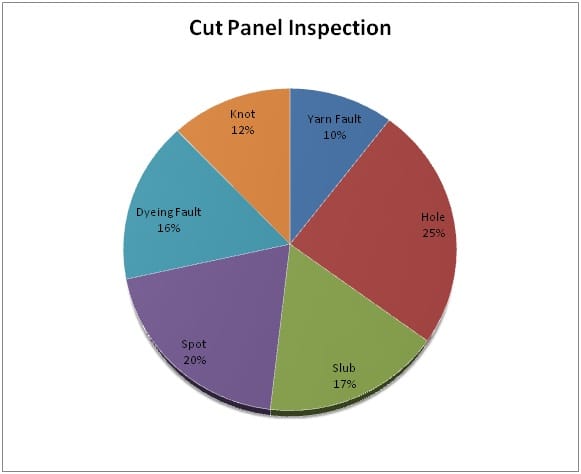
4.1 Pie Chart
4.2 Result and Discussion
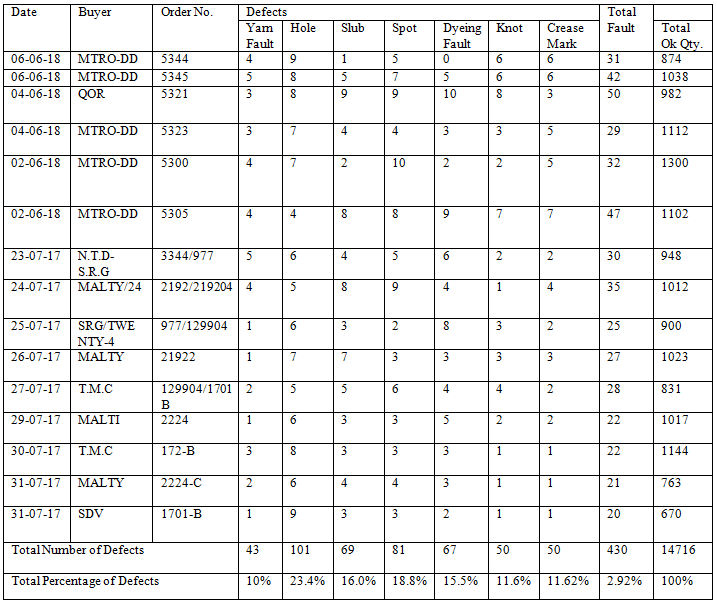
For the analysis of these big data, almost 15146 no of data was inspected. Among them, around no. of 430 cases were out of mark due to cutting issue. Andthese were found when the cut panel inspection were being done. Meanwhile, no. of 14716 cases were okay to work, which implies the percentage of fault 2.92.
However, a brief is being mentioned below-
- In fabric hole the most fault was found 101 from 14716. So, the total fault percentage found 23.48%.
- The main fault is from fabric hole problem that was almost 101 out of 14716 no. of cases and it was 23.48%.
- Different types of fault (such as dyeing spot, ironing spot, bleaching spot etc.)found 81 pieces from 14716 and total fault percentage 18.83%.
- From the dyeing problem found 81 cases among 14716 and in percentage it was 18.83%.
- For slub we found 69 pieces from14716. Fault percentage is 16.04%
- Sluby issue causes 16.04% of cut panel rejection.
- From 14716 pieces we found 50 faults For Knot and crease mark. Total fault percentages are 11.62%.
- Crease Mark issue causes of 11.62% rejection of cut panel.
- The lowest fault we found for yarn fault 43 from 14716 pieces. Total fault percentage for yarn fault is 10%.
- Finally, the lowest fault is from Yarn fault which implies the percentage of 10.
4.3 Causes and remedies of fault
Fabric Hole (24%): During Inspection when found any large or small hole in the fabric is called fabric hole.

Causes:
- Holes are the results of yarn breakage
- Yarn tension too high
- Presence of knots in yarn
- If the yarn count is not correct
Remedies:
- Yarn strength must be sufficient
- Maintain proper tension
- Knots should be given properly
- Use proper count of yarn
Spot (20%): Improper Ironing, dyeing shade, bleaching and dyeing spot are found in fabric is called dyeing spot.

Causes:
- Operators not correctly mixing and thoroughly dissolving the dyestuff, in the right amount of water, most often cause these.
- Dye bath hardness.
- Not agitation of dyestuff.
- Dirt, dust and other impurities can be the causes of spot.
- Dirt and dust in the iron surface can be the cause of spot
Remedies:
- Use adequate amount sequestrate to lower bath hardness.
- Proper agitation.
Slub (17%):
Usually caused by an extra piece of yarn that is woven into fabric. It can also be caused by thick places in the yarn. Often is caused by fly waste being spun in yarn in the spinning process. For Knit Fabric Usually caused by a thick or heavy place in yarn, or by ling getting onto yarn feeds.

Causes:
- Accumulation of fly and fluff on the machine parts.
- Poor carding and combing.
- Defective ring frame drafting and bad piecing
- Improperly clothed top roller clearers.
Remedies
- Machine surfaces to be maintained clean.
- Proper functioning of roller clearers to be ensured.
- Broken teeth gear wheel to be avoided and proper meshing to be ensured.Clean the fabric and Iron surface.
Knots (12%): Knot is Fastening made by tying together the ends of yarn is called knots.

Causes:
- When thread breaks during process of winding, warping, sizing or weaving
Remedies:
- Basically, Not mendable.
- Proper tension of thread during winding, warping, sizing, or weaving.
Dyeing Fault (16%): Dyeing fault means operational problem, such as uneven dyeing, shade variation, dyeing spot etc. we found uneven dyeing in our working area.

Causes:
- Uneven pretreatment (uneven scouring & bleaching).
- Improper color dosing.
- Using dyes of high fixation property.
- Uneven heat-setting in case of synthetic fibers.
- Lack of control on dyeing m/c
Remedies:
- By ensuring even pretreatment.
- By ensuring even heat-setting in case of synthetic fibres.
- Proper dosing of dyes and chemicals.
- Proper controlling of dyeing m/c.
Crease Mark: Crease mark appears where creases are caused by fabric folds in the finishing process

Causes of faults:
- Improper motion of padder
- Improper fabric movement
Remedies:
- Proper motion of padder
- Ensure smooth running of fabric
- Use anti-creasing age
Yarn fault (10%):
Missing Yarn: Occurs in warp knit. Reuslts from wrong fiber yarn (or wrong size yarn) placed on warp. Fabric could appear as thick end or different color if fibers have different affinity for dye.
Causes:
Yarn breakage due to any reason and not pass through the yarn guide. It may be occur for tension variation.
Remedies:
Yarn guide and tensioner must be used.
Conclusion
Cutting quality control of garments, cutting section plays a vital role in garments because right measured cutting is required to get the right shape of garments product. Proper cut panel inspection after cutting fabric can give high quality product.
In cutting section, defect percentage is fabric hole is higher 23.41% the major defect is ‘fabric hole’ and all defects are replaced by re-cutting. This problem is happened for needle and yarn count variation. By reducing yarn, breakage during knitting it can be reduced. So we can undoubtly said that cut panel inspection has great impact to maintain quality of garment.
References:
- Managing Quality in the Apparel Industry by Pradip V. Mehta and Satish K. Bhardwaj
- Garments Technology by Prof. M. A. Kashem
- Understanding Textiles For a merchandiser by Engg. Shah Alimuzzaman Belal
- Garment Manufacturing Technology by Md. Shafiul Azam, Md. Abu Saleh & Khondokar Abu Nafiz
- 1.http://www.bgmea.com.bd/home/pages/aboutgarmentsindustry
- http://fashion2apparel.blogspot.com/2016/12/quality-control-garment-factory.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/Mdabdullahalfaruk/production-and-faults-in-cutting-sewing-finishing-in-a-knit-garment-industry
- http://textilelearner.blogspot.com/search/label/Garments%20Manufacturing
- http://www.goldnfiber.com/2013/04/sop-of-fabric-layer-cut-panel-inspection.html
- http://gmtmerchandisng.blogspot.com/2015/01/fabric-inspection-procedure-and-cutting.html
- https://www.slideshare.net/sheshir/knitted-fabric-faults-and-their-remedies
