The textile manufacturers in the world are looking for new ways to improve their processes to keep up with the rapidly changing industry. Automation is one of the most reliable technologies for responding to changes quickly. With the right tools, we can change a product line in hours, days or weeks. Not many months as with other forms of automation. Today we will try to discuss about automation in textile printing and finishing.

Automation in Textile Printing and Finishing
Print Paste Automation
In dye house, the printing sector uses dyes & pigments in the form of powder or liquid in the printing process. In fact, 90% of printing uses only powder, like Reactive dye or Disperse dye. Only 10% use liquid dyes for printing. Liquid dyes need separate tank to store and also need to be kept in constant circulation so as to avoid sedimentation and spoiling of the entire batch. So, in both cases the dye preparation process is one that needs proper care.
Some Issues that are Faced by Printing Department:
- Excess prepared print paste goes waste.
- Stored print paste becomes hard and may not be made fluid again.
- A big area is required for storing the complete print paste carboys for the entire day’s printing.
- Human error in handling the print paste.
- Inconsistency in print paste preparation.
These color preparation challenges can be easily overcome by installing an appropriate Automatic Print Paste Dispensing System in a dye house in printing department.
Automatic Dosing System
Color Service has an innovative solution that allows a printing department to use both powder and liquid dyes in the same dosing system. The Color Service automatic printing color kitchen is composed of two main units- a thickener depending on the quantity of print paste required, the unit picks up a drum and delivers it to an initial thickener dosing head. For liquid dyes such as pigments, dosing can be done with the same thickener dosing head. But in case of powder dyes, the drum goes to a powder dosing unit on a conveyer. After ending of powder dosing, the drum goes back to print paste dosing unit. The drum is move to the next stage to complete the remaining amount of thickener.
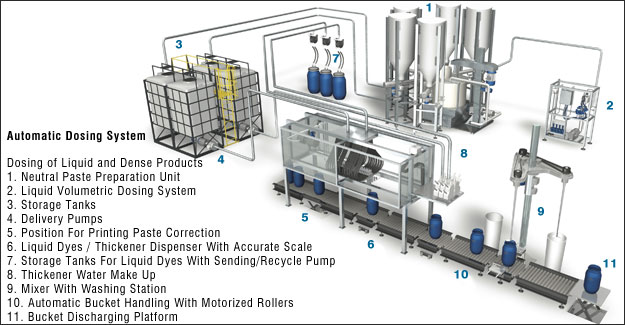
Advantages of Print Paste Automation Dosing System:
- Reduction of chemical and pigment wastage.
- Human errors have decreased.
- It takes less time than before.
- Expenditure has been reduced comparatively and energy wastage has been reduced.
- The production rate i.e. work efficiency has increased as compared to the past.
- Required less man power.
- Lower labor cost.
- Backward tracing.
The demand for printing paste automation is increasing day by day with the growing demand of rotary and flatbed printing machines. It is quite clear that in order to achieve high quality and increase productivity in green field projects, it is necessary to install modern technology printing machines and print paste automation dosing systems.
Some Automatic Fabric Printing Machinery
Different types of fabrics are required for printing and designing. Ink/color transfer and color retention depend on the strength of the fabric. There are many types of fabric printers that work according to their own list of pros and cons to produce huge garments. These automatic machines are manufactured for increased efficiency and different levels of detailing on garments. Here are some of the best fabric printers-
Mutoh VJ-1938TX: This fabric printer is a best choice for new manufacturers to go with as it provides excellent fabric printing when it comes to entry-level and mid-level production. In this printer, ink choices are flexible and it will be perfect if maximum works involve woven fabrics.
Mimaki TX300P-1800B: This printer is extremely user-friendly and has a level of technical finesse that makes it possible for this machine to monitor its activity and performance. This is a vital component for printing on delicate and knitted fabrics.
Mimaki TX300P-1800: The 1800 Mimaki model is also very extremely user-friendly and simple enough to operate and maintain. However, unlike the 1800B, this fabric printer doesn’t associate with an adhesive print blanket. Hence, it is very difficult to print on delicate fabrics using this specific model.
You may also like: All Over Printing (AOP): A Fast Growing Sector in Bangladesh
Fully Automated Flat-Bed Screen-Printing Machine
In order to extend the speed of flat-bed screen printing, it had been imperative to devise a technique of printing all the colors simultaneously. This entails each color application position being fixed while the substrate moves. The color is applied through the screens while the frame is stationary. Flat-bed screen printing machines where the fabric remains stationary and the screen moves on a carriage have also been developed for the printing of silk. The entire operation is controlled pneumatically.

Top 10 Automatic Screen-Printing Machines:
- M&R Stryker Automatic Oval Screen-Printing Press
- MHM Synchroprint 5000
- ROQprint ECO P18 XL
- Brown Electra Print Automatic Textile Printer
- MHM IQ-Oval Compact
- Workhorse- The Sabre Series
- RPM Revolution series
- Tas Hawk HX20
- Anatol VOLT XL Screen Printing Machine
- Printex Hurricane SL
Robot Printing and 3D Fiber Structure Printing
Printing designs onto fabric is a core task in garment manufacture. In many cases, the printed design is the only difference between related product lines. Robots are perfect for printing and drawing as the complex paths can be programmed automatically if we’re using the right tools.
One of the latest developments in robotic textile manufacturing is 3D Printing. In a similar manner to normal 3D printing, 3D printed fabrics use fibers that are coated in polymer for garments like protective fire-fighting uniforms. The robot guides the material (fabric) into the appearance of the 3D structure and therefore the hardening polymer sets it in place.
Automation in Textile Finishing
Automation is not something new in textile finishing, it has been used for a long time, but over time it has become more modern. Automation is significant in machine control systems, robotized systems, color analysis, etc. Modern automation technologies show great potential for textile finishing based on electrical, electronics, computer programs and smart systems. At present, three reliable things are being done to achieve important goals like product flexibility and quality-
- Automatic standardization of goods/equipment.
- Automatic adjustment of systems.
- Popularity of personal computer in the field of textile finishing.
The automated standardization of components takes place due to the concentration of automation technologies in some basic forms of automated processes which must be done by the mechanical forces by machine. The machine is defined and summarized by a system made of inputs and outputs for an automated textile production system. The inputs of textile production are sensors which transform the physical variables of the system into electrical values. And the outputs of automated production are the actuators controlling the machine and consequently the process.

The main difference between automated textile finishing systems essentially lies within the quantity of variables controlled. The most influential issues in textile finishing through technological development are-
- Color analysis.
- Process control.
- Production control system.
- Color kitchen.
- Automated inventory control systems.
- Transport and robotized systems.
- Machine control systems.
Conclusion
The textile market has been one of the most growing and robust industries and it has only continued to grow. Fashion is consistently evolving and then, it only is sensible for the clothing industry to alter with it. The advent of technological advancements in the apparel market has made room for automation machinery and has given garment production a great boost while also making it cost effective. Automation in fabric printing and finishing have made it possible for manufacturers to mass produce clothes with great precision and in less time.
References
- https://textilelearner.net
- Fiber2fashion.com
- Batechindia.com
- Fiber2fabrics.blogspot.com
- Robodk.com
- Imprintnext.com
- Gulrajani, M.L. (Ed). 1993. Methods of Printing in Chemical Processing of Silk by Chopra, S. Textile Department, IIT, Delhi.
Author of this Article:
Md. Imran Hossain
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Shahid Abdur Rab Serniabat Textile Engineering College, Barisal.
Email: mdimranhossain.te@gmail.com
Articles published by same author:
- Application of Automation in Dyeing Industry
- Automation in Textile Industry: Impacts, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Applications and Impacts of Automation in Fiber and Yarn Manufacturing
- Application of Automation in Weaving Industry
