What is Chemical Spinning?
Chemical spinning operations are generally used to make man made filament fibers to yarns by converting the fiber forming substance to a viscous fluid that is extruded through the holes of a spinneret and then solidified by coagulation or evaporation or cooling. This process is known as chemical spinning to distinguish it from mechanical spinning. A filament fiber is the fiber which comes in continuous lengths for use. All the man made fibers and silk is filament in nature. The man-made fibers can also be cut into staple length and spun on usual spinning system for the spun yarn production. The filaments are spun by chemical spinning which includes the process of extruding the polymer extrusion through the spinneret. These filaments are solidified in fiber form. These solidified filaments are brought together and are slightly twisted to produce filament yarns. The different types of chemical spinning are as follows:
Types of Chemical Spinning:
- Wet spinning
- Dry spinning
- Melt spinning
Above three types of chemical spinning methods are described below:
1. Wet spinning:
This method of spinning is more suitable for rayon fibers. The procedure of spinning involves the extrusion of an appropriate liquid solution through the spinneret in a chemical bath that coagulates the solution into filament strands. These filament strands are then drawn out of the bath, washed and dried before being wound on the spools. The fibers are spun in the chemical bath and hence called as wet spinning.
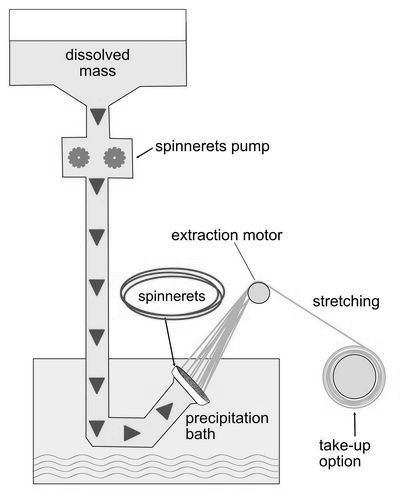
In wet spinning, the polymer solution passes through a metered pump; this allows a measured amount of the solution to pass through to the spinneret.
The spinneret is submersed in a coagulating bath to neutralize the filaments and set them. The filaments are then drawn, which extends the length of the fiber. This lengthening makes the fiber stronger because the atoms inside the fiber become aligned. The filaments are then wound onto bobbins. This process is used on viscose, lyocell, some acrylics, modacrylics and elastanes.
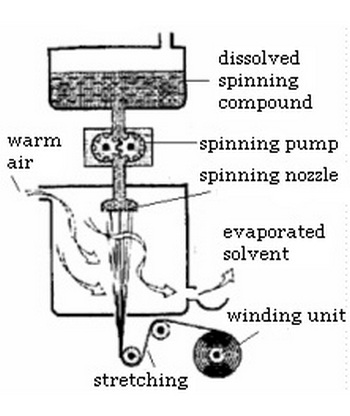
2. Dry spinning:
The process involves the extrusion of the suitable liquid solution through the spinneret into an air chamber. The air reacts with the extruded streams causing them to solidify twisted and/or processed further and then wound onto spools. This method of spinning is used in manufacturing of acetate yarns.
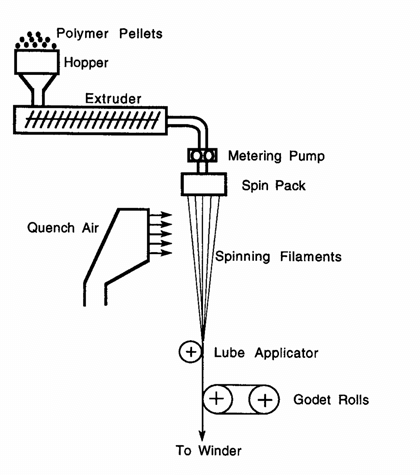
3. Melt spinning:
Melt spinning uses the heat to melt the polymer to a viscosity suitable for the extrusion through the spinneret. As the name indicates the chips of fibers are melted and extruded through the spinneret to obtain the fibers. It is used for the polymers that are not decomposed or degraded by temperatures necessary for extrusion. Polymer chips obtained from previously reacted chemical combinations are melted and then pumped through a spinneret in an air chamber. The extruded stream cool and solidify into continuous filaments and are then drawn out of the chamber twisted and/or processed further and subsequently wound onto spools. This method of spinning is suitable in manufacturing the polyester yarns.
Types of Specialty Spinning:
- Bicomponent spinning
- Biconstituent spinning
1. Bicomponent spinning:
Bicomponent spinning involves the extrusion of two different types of the same polymer through the spinneret. Bicomponent extrusion can be simply thought of as two spinning machines working one inside the other.
There are three different techniques of bicomponent fiber production. One method is the side-by-side extension through one spinneret hole of two varieties of same polymer. As the two variants cool and solidify they adhere together as one filament. The filament is composed of both the fibers. For eg. – when nylon 6 and nylon 6.6 solutions are extruded through one spinneret hole, a filament is obtained which consists of both the polymers attached side by side. Thus the yarn obtained exhibits the characteristics of both nylon 6 and nylon 6.6.
Another means of manufacture of bicomponent is basically that of using one spinneret inside another. One variant of the polymer is pumped through the center or core spinneret while another is pumped though the outer or surrounding spinneret. Both varieties of polymer emerge as one through the common hole of the surrounding spinneret so that the fiber is formed of a core of one polymer variant surrounded by a ring of another variant.
The third method of composition of bicomponent fibers is the distribution of drops of one molten polymer variant into another molten form of the same polymer. This composite mixture is then extruded through the single spinneret hole. The result is a matrix or conglomerate, of minute short strands of one fiber suspended inside another variety of the same fiber.
2. Biconstituent spinning:
Another variation of filament yarn production is biconstituent spinning. The biconstituent spinning involves the extrusion of two different polymers through the spinneret. The method of extrusion is similar to that of bicomponent spinning. The filament can be obtained by any of the three methods mentioned above. An example of biconstituent spinning is a fiber which contains two different polymers like that of polyester with nylon.
You may also like:
- Kevlar: A Fiber has changed the War Industry
- Ceramic Fiber: Properties, Production and Applications
- Properties, Manufacturing and Application of Fiberglass
- Properties, Manufacturing and Application of Ultrafine Fiber
