Features, Characteristics, Derivatives and End Uses of Twill Weave
Md. Rubel Miah
Department of Textile engineering
World University of Bangladesh
Email: rubel099@gmail.com
What is Twill Weave?
Twill weave is a kind of weave that repeat on three or more ends and picks and produces diagonal line on the face of fabric. In a regular twill the diagonal line or twill line produces at 45-degree angle with the horizontal.
Twill weave is second basic weave from the production and using point it views, it is also in second position. Mainly the fabric painting is made it the structure. Example, Denim fabric (3/1) made it twill weave.
Features of Twill Weave:
The main feature of twill weave are mention bellow:
- Diagonal line can be seen on the faced of the fabric.
- Twill line may be from lower lift to upper right (Z-twill) or from lower right to upper lift (S-twill) corner.
- Smaller repeat twill is (3) It means take at least end and three picks produce twill weave.
- Three or more heald shaft are required for shedding.
- Generally straight draft is used for twill weave besides this pointed or v draft is also used.
- Appearance it will design can be seen from both rides the fabric.
- Diagonal lines run at angle vary between (15-75) Degree but in a continuous or regular twill is 45 degree.
Characteristics of Twill Weave:
Twill is characterized by the diagonal weave pattern on the face of the fabric.
- May have face/back and up/down orientation
- Interesting surface and texture
- Seldom printed
- The soil is less evident
- More pliable
- Better wrinkle recovery
- High counts possible (more durable)
- More expensive
- Wale may be prominent
Twill Angle:
Twill angle is the angle which is produced by twill line with respect to the horizontal line. This twill angle depends on following factors.
- Ratio between EPI and PPI.
- Difference between warp and weft count.
- Rate of advancement it interlacement warp and weft.
This twill angle is denoted by, θ
![]()
Suppose rate advancement twill in both upward and outward =1, EPI and PPI in both direction = 36
θ = Tan-1(1) = 1
Classification of Twill Weave:
Twill weave is can classified various ways they are mention below,
1. According to direction of twill line on the faced of fabric.
2. According this aspect there are two type of twill weave namely.
- S -twill: Down word displacement of twill line from upper left to lower right corner.
- Z- twill: Upward displacement of twill line from lower left to upper right corner.
3. According to faced yarn: there are three type of twill weave according to faced yarn namely:
- Warp faced twill: For example, twill.
- Weft faced twill: For example, twill.
- Balanced twill: For example, twill.
4. According to nature and twill line: There are three type of twill weaves,
- Sample warp or weft twill: It every warp thread passes under only one weft called simple warp twill. For example, twill are simple are warp twill again it every weft thread passes over only one warp thread in twill weave, that is called simple weft twill. For example, twill are simple weft twill.
- Expended twill: There is no one up or one down in this type of twill.
- Multiple twill: If in a fabric there are more than one twill line in the repeat, it is called multiple twill.
Factor Affecting the Prominence of Twill Weave:
The following factor affecting the prominence of twill weave
1. Feature of weave
The prominence of twill line on feature of weave in the following ways;
- The twill of short floats less prominent twill line.
- The twill line of long float more prominent.
2. Characteristic of yarn:
It influence twill line as bellow:
- Twill off course and soft twisted yarn→ More prominent twill line.
- Twill of fine and more twisted yarn→ Less prominent twill line.
3. Thread per inch (TPI):
More number of ends or picks per inch causes more prominent twill line.
4. Direction of twill line in relation to yarn twist direction:
When direction of twill on fabric is opposite to the direction of twist in yarn the twill line becomes more prominent and vice-versa.
Derivatives of Twill Weave:
There are many derivatives of twill are given bellow;
- Zigzag/waved/pointed twill weave.
- Hearing bone twill.
- Diamond design.
- Diaper design.
- Broken twill.
- Elongated twill.
- Stepped twill.
- Shaded twill.
- Combined twill.
- Diagonal design.
- Elongated design.
A. Zigzag/waved/pointed Twill Weave:
It is the simplest and one of the most important modifications of twill weave produced by reversing the direction of twill at suitable interval
A point is selected (usually the last warp is selected) as the reversing point and so it is sometime call as point twill. In this twill pointed or straight draft is used.
This twill is produced by combining S and Z twist. According to reversing of direction there are two type of zigzag twill:
- Horizontal zigzag twill.
- Vertical zigzag twill.
1. Horizontal zigzag twill:
When the reversal direction of twill line occurs upon the warp yarn, it results a horizontal zigzag twill, Here the basic twill is extended in warp direction. Here the number of warp yarn in a repeat is double of the number of wefts. In horizontal zigzag twill pointed draft is used.
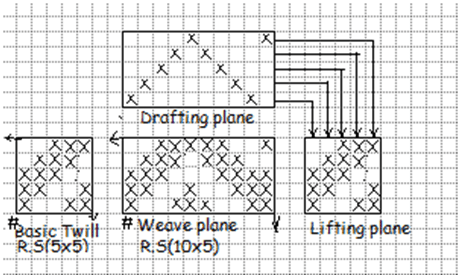
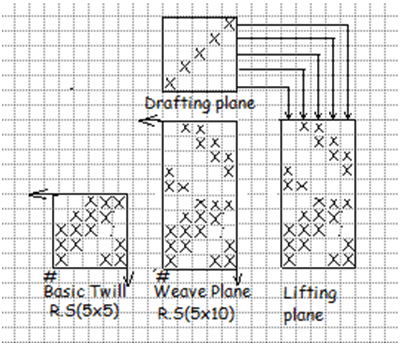
2. Vertical zigzag twill:
When the reversal direction of twill line occurs upon the weft yarn, it results a vertical zigzag twill, Here the basic twill is extended in weft direction. Here the number of weft yarn in a repeat is double of the number of warp. In Vertical zigzag twill straight draft is used.
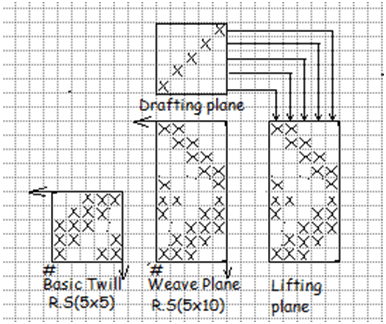
B. Hearing Bone Twill:
This twill are constructed in a different manner from the ordinary zigzag twill. Though it also depend on reversal of twill direction
Here reversal direction occurs after a middle line. Here at first the basic twill is drown then the number of central point is selected in zigzag twill. Rather in extended second half of basic twill the following matter happened.
- The floating point of first half become down in second half.
- The down of first half become floating in second half.
In hearing bone twill straight draft is used. There are two type of hearing bone design
- Horizontal hearing bone twill.
- Vertical hearing bone twill.
1. Horizontal hearing bone twill:
When hearing bone twill is created by extending the basic twill in warp direction, horizontal hearing bone result in.
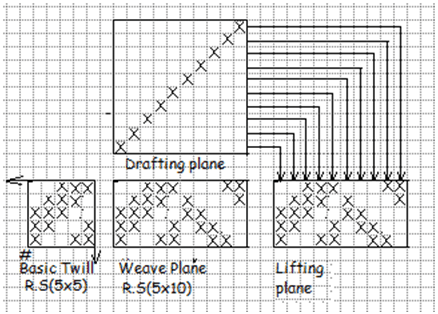
2. Vertical hearing bone twill:
When hearing bone twill is created by extending the basic twill in weft direction, horizontal hearing bone result in.
C. Diamond Design:
It is a derivatives of twill weave. It constructed on the bans of zigzag twill principle. It is obtaining by combining a horizontal and vertical zigzag twill. So here in the repeat the number of both warp and weft thread are double then that in basic twill.
Diamond design geometrical about their vertical and horizontal axis. In this weave pointed draft is obtained.
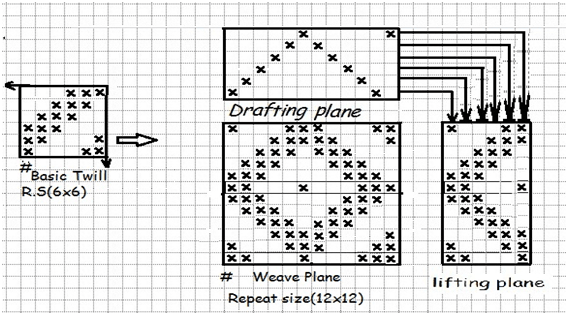
To contract a diamond design at first the design repeat is selected. It the basic twill is 3 up 3 down, that is 6×6 insize, the repeat of design will be 12×12 insize.
Uses: Towel, Bed cover, Table cloth, Pillow cover etc.
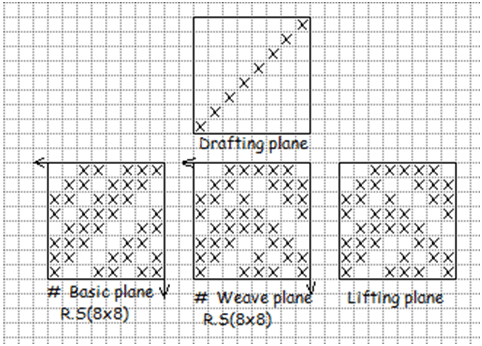
D. Diaper Design:
This derivative of twill weave is created on the basis herring bone principle. This design is constructed by combining horizontal and vertical hearing bone twill.
In the repeat of a diaper design the number of warp and weft threads are two type more than that in its basic twill. So, if the basic twill size is 8×8.Its diaper design repeat size will 16×16. In case of diaper design, Broken or straight draft is used
Use: Same diamond.
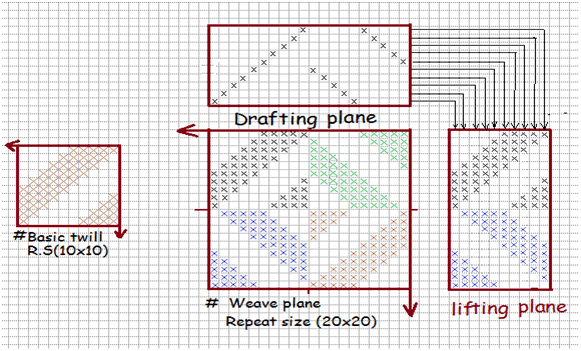
E. Broken Twill:
This is obtaining by breaking the twill line of a regular twill It is somewhat similar in appearance Zigzag twill
Broken twill can be obtained in different ways. At first basic twill is divided into two section then the first section unchanged and the second section is reverse ii its order, that is to say if the basic twill is made up of 8 warp threads namely1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 then its broken twill derivatives will obtain the order 1,2,3,48.7,6,5.
Broken twill can be of way and increase of broken twill straight and Broken draft is used.
F. Elongated Twill:
The twill angle from in cloth depend upon,
- The relative ratio of ends and pick per unit length.
- The rate of advancement of one interlacing with respect to the following one.
Normally the twill angle is 45 degree where the end and pick per unit area are equal. But in elongated twill, the twill angle more or less than 45 degree any twill design without twill angle.
Elongated twill can be formed in two different ways:
(a) With the help of step number.
(b) By selecting stating of elongated twill with a base line.
(a) With the help of step number:
If the step number of elongated twill is two, then by taking only odd number of warp thread from the basic twill here the warp number in step twill will be equal to the basic twill.
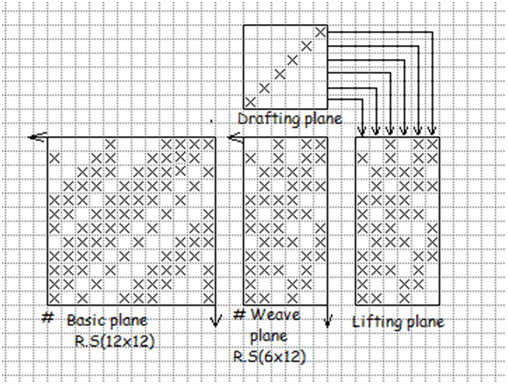
(b) By selecting stating of elongated twill with a base line:
Here at first a step number is to be selected. In such a way that the repeat of base line become divisible by that step number.
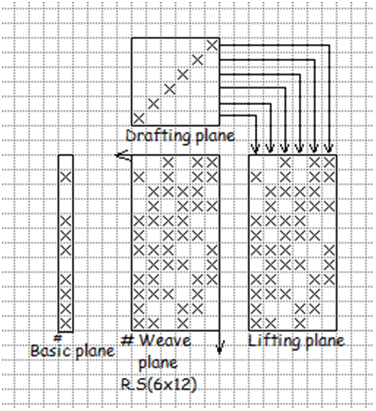
For example, for a twill with formula number the repeat size will be 14×14. If we select move number as 2 then in produced elongated twill the number number of warp thread will be 7 and that of weft thread will be 7 in case of weft faced twill.
G. Stepped twill:
Stepped twill is produced by stepping a continuous twill. This are two type stepped twill,
(a) Warp way stepped twill.
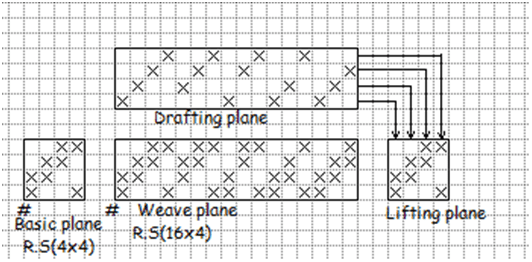
(b) Weft way stepped twill.
- Warp way stepped twill: Here stepping is done in warp way.
- Weft way stepped twill: Here stepping is done in weft way.
H. Shaded Twill:
By shaded twill we can create shade effect on fabric the shade effect is created by the combination some thick to thin twills or thin to thick twills.
The shaded twill are of following type,
1. Single shaded twill:
Here the shade effect become thick form thin once after being thick it again starting to be thin and thus complete the whole repeat. For example
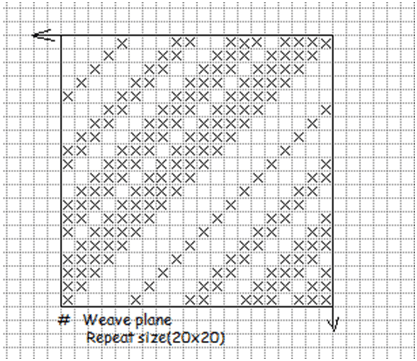
2. Double shaded twill:
Here the shade starts form thin to thick and again it become thin. For example,
Benefits of Using Twill Weave Fabric:
There are lots of benefits for using twill weave. Some important benefits of using twill weave fabric are given below.
- Durable: Twill fabric is very durable and can withstand a lot of wear, making it a great fabric for clothing and upholstery.
- Opaque: The twill weave fabric does not create a sheer quality, so all twill fabrics have great opacity, making them great for curtains, housewares, and clothing.
- Shows few wrinkles and creases: Twill fabric doesn’t wrinkle very easily because of the thickness of the material.
- Shows few stains: The direction of pattern helps hide dirt and stains from view, so spills at home or on clothes are disguised more easily.
- Drapes well: Twill fabric has a nice drape for clothing, sheets, and more.
End Uses of Twill Weave Fabric:
Twill weave are extensively used in manufacturing cloth for garments household cloth and industrial cloth.
- Generally, diamond, diaper and zigzag twill are used for making pillow, cover, screen, upholstery, bed sheet, towel etc.
- Continuous twill are used for making fabric for shirting, suiting and pant in (denim, gaberdine).
- For making various type of ornamental cloth, other derivatives of twill weave are used.
- Hearing bone twill are used in the cloth of suiting and overcoats.
You may also like:
- Construction of Shedding Tappet for Plain and Twill Weave
- 100 Different Types of Fabric and Their Uses
