What is Garments Dyeing?
Garments dyeing process is a new technology for us but it is actually using in the European countries for last 70 years. It is the process of dyeing fully fashioned garments subsequent to manufacturing, as opposed to the conventional method of manufacturing garments from pre-dyed fabrics. At first this technology applied on woolen and silk garments but now it is applied on polyester, nylon, acrylic and also extensively on cotton garments. Popularity of garment dyeing is increasing in France, Italy, Spain, Germany, Canada, Turkey, Israel, South Africa, Japan, USA and UK etc. counties.
In garment dyeing, fully fashioned garments such as pants, sweaters, shirts and skirts are dyed after manufacturing is completed. Most garments are made of cotton or a cotton-rich blends which may contain other fibres such as wool, nylon, silk, acrylic, or polyester as a minor component in the blend. Traditionally, garments are manufactured from pre-dyed fabrics before the cutting and sewing. Garment dyeing has been gaining importance and popularity due to cost savings and fashion trends in recent years, and will continue to grow in the future.

Garment dyeing, one of the finishing operations, allows the manufacturer to produce special colour effects that may not be feasible from continuous processed fabric. The demand from retailers for rapid response to fashion and colour changes has resulted in some speciality garment manufacturers producing products that can meet these requirement using fabric that has been previously prepared for dyeing when the garment is made. The made-up garments are then processed to their respective colours by specialised garment dyers. Thus, short runs of a specific product are therefore possible with the advantage of more economical garment production when only an uncoloured fabric is being used. This reduces wastage and lowers the cost of stock, when only a single fabric type is required.
Normally we dye fiber, yarn or fabric and then the dyed and finished is used for making garments. In case of garment dyeing, the garments are made from grey fabric and then the garments are dyed in required color and shade.
The garments which are dyed in garments dyeing technique are as follows:
- Active wear
- Jeans item
- Panty-hose
- Shirt
- Slacks
- Terry items
- Dresses
- Leisure or loungewear
- Pullover
- Skirt
- Socks
- Sweater etc.
Popularity of garment dyeing is increasing day by day all over the world as well as in our country also. There are many advantages of garment dyeing which are the reasons of its popularity increase.
Advantages of Garments Dyeing:
There are many advantages in garments dyeing over fabric dyeing in case of solid color garments production and export trade. The important advantages are summarized below:
- Comparatively lower cost of production for any item of any color and shade.
- Comparatively less time is required to produce and supply garments.
- No possibility of shade variation within the garments.
- Small lots of different items could be produced at lower cost within less time.
- Old garments could be redyed, hence becomes like new garments.
- Desizing, scouring, bleaching, dyeing and finishing could be done in the same machine.
- Comparatively lower capital investment cost to set-up a garments dyeing project.
- In some cases, lower liquor ratio in garment dyeing requires lower water, steam and chemical consumption, hence lower garments dyeing cost.
- During fabric cutting approximately 15% fabric is cut out as wastage, if this 15% fabric is cut out as grey fabric rather than colored fabric, then the wastage cost will be saved.
Precautions to be taken before Garments Dyeing:
Garments made from cotton grey fabric are dyed in garments form in the garments dyeing machine. Before garments dyeing some precautions are needed to avoid dyeing problems that may occur during garments dyeing. The precautions are discussed below:
- Garments design should be made from engineering point of view.
- If garment is made after desizing, scouring and bleaching of grey fabrics and then dyed in garments form, then the possibility of problems will be reduced.
- If possible, garments should be made from the grey fabrics of the same lot and same source.
- The seams should not be too tight or too loose especially in the areas containing elastic like waistband, cuff etc. which may create irregular dye penetration resulting irregular dyeing.
- The garments which are produced from woven and knitted fabrics combindly, the knit fabric should be pre-shrunked, otherwise seam pucker may develop after garments dyeing.
- If the garment fabric is of mixed fibers, during garments dyeing, dye selection should be done carefully, having equal dye pick-up to avaoid irregular dyeing.
- Poor quality metals should not be used as accessories in the garments, which may be damaged during dyeing by the action of salt and alkali. If any metal component is used in the garments should be made from nickel or its alloy.
- Sewing thread used for making the garment should be of same fibre like the garment fabric, otherwise color difference may occur between garments fabric and sewing thread.
- Buttons used in the garments should be selected carefully. Buttons made from casin, cellulose, nylon etc. may be damaged during garments dyeing but polyester button is safe in this respect.
- If elastic is used in the garments and the elastic is made from natural rubber or polyurethane fiber like lycra may create problem during garments dyeing. To avoid such problem dye should be selected made of copper free. During bleaching, polyurethane fibers may be damaged by the chlorine. Polyester type elastomeric fiber is safe in peroxide bleaching.
- Interlining is used in most garments. Only those interlinings should be used in the garments to be dyed only recommended for garments dyeing, otherwise the performance of interlining may be destroyed.
- The garments made from compactly woven cotton fabric should be dyed with hot brand reactive dyes, otherwise problem of irregular dye penetration may occur.
- For some specific color, if specific dyes are used then the dyeing cost will be lower. For example, navy-blue and black color could be produced in the garments by using sulpher dyes at lower cost.
- Presence of mineral impurities in the cotton fibers may vary wich may impede the stability of peroxide liquor during bleaching with hydrogen peroxide. Even insoluble compounds may form during hydrogen peroxide bleaching. Those insoluble compounds may redeposit on the garments fabric resulting spots on the fabric. Special chemicals are available to avoid such problem.
- Crease marks may develop in the cotton garments during dyeing. To avoid such problem, special chemicals like “Imacol brand” may be used.
Selection of Interlining before Garments Dyeing:
Garments to be dyed after manufacturing, needs careful selection of interlining. As because, during garments dyeing, performance of interlining used in the garments may be destroyed due to effect of chemicals and temperature used in the dye bath. To avoid such problem, interlining for the garments to be dyed should have following properties:
- Interlining used in the garments should take-up equal amount of dye and chemicals, as the garment fabric takes-up.
- Due to garments dyeing, bond strength between interlining and garment fabric should be undisturbed or unaffected.
- Handle properly of the interlining attached areas of the garment should be as per expectation.
- During garments dyeing, resin present in the interlining may pick-up dye molecules, hence color depth problem should not arise in the interlining areas of the garment with remaining areas of the garment.
In the readymade garments manufacturing industries, fusible interlining is mostly used for making the garments. The fusible interlining is composed of following three types of materials: a) Base fabric, b) Base fabric finishing & c) Resin coating.
During garments dyeing, the role of those three components of fusible interlining are discussed below:
a) Base fabric:
For the manufacture of cotton garments, fusible interlining made from cotton base fabric is always preferred. Because, during garment dyeing, garment fabric as well as interlining base fabric, if both are made from cotton, then the dye pick-up will be equal. As a base fabric, cotton woven fabric is used but non-woven cotton fabric can also be used. If non-woven fabric is used as base fabric for the interlining, then those non-woven base fabric should have the following properties:
- If any resin used as binder for the non-woven fabric production, should not create any problem to dye penetration.
- During garments dyeing, due to dyeing effect, nonwoven base fabric should not change its original dimension.
- Due to garments dyeing, property of nonwoven base fabric should be unaffected.
b) Base fabric finishing:
If cotton fabric is used as base fabric for the manufacture of fusible interlining then, normally the base fabric is finished with resin. Dimethylol urea derivative base resin is normally used for cotton base fabric finishing, which creates problem during garments dyeing. Because it creates problem to dye penetration during garments dyeing. If the base fabric is mechanically shrunked and low formaldehyde resin is used for base fabric finishing, then the problem of dye penetration will be reduced. If cotton base fabric for the manufacture of fusible interlining is only mechanically shrunked finished, then the problem of dye penetration could be avoided. Moreover, there will be no problem of differential shrinkage of cotton base fabric and cotton garments fabric.
c) Fusible resin coating:
Various types of resin coating is used for the manufacture of fusible interlining. After attaching the fusible interlining into the garments, if the garments are dyed, some time problem may arise into the fused areas of the garment. During garments dyeing, due to the effect of dyeing temperature, chemicals used in the dye bath and longer period of agitation onto the garments, splitting of the interlining fabric and garment fabric may occur by breaking bonding between those two fabrics.
The resin used for the resin coating of the fusible interlining should be hydrophobic type and melting temperature of the resin should be more than 140 0C to avoid such problem. Polyethylene and polyolifin type resin works well in garment dyeing.
Methods of resin coating also plays role in this respect. If scattered coated fusible interlining is used in the garment, then during garment dyeing blister may form into the fused area of the garments. Hence dot coated fusible interlining is better to use in the garment to be dyed.
Garments Dyeing Machine:
For more than last 60 years, continuous research and development is going on garments dyeing technique, process and machines. Various types of garments dyeing machines have been developed and all those garment dyeing machines can be classified into following two groups:
- Pedal dyeing machine
- Rotary dyeing machine
A brief discussion on both types of garments dyeing machines are done below:
A. Pedal garments dyeing machine:
Pedal type garments dyeing machine is the first and oldest type of garments dyeing machine still used in the European countries. Pedal type garments dyeing machines are two types that is overhead pedal type and side pedal type.
Pedal type garments dyeing machines are used for the woolen knit wear type garments dyeing. Dyeing cost is higher in pedal type garments dyeing machine due to manual operation, higher labour load, manual loading and unloading of garments, manual chemical feeding etc. reasons. This pedal type garments dyeing machine is not used in any garments dyeing industry of Bangladesh.
B. Rotary garments dyeing machine:
Rotary garment dyeing machine is the modified version of pedal type garment dyeing machine. Rotary garment dyeing machine are of two types: Normal atmospheric pressure type (less than 1000C) and high temperature type (More than 1000C dyeing temperature). The high temperature type garments dyeing machine is microprocessor controlled machine, which is not still used in Bangladesh.
1. Atmospheric pressure rotary garments dyeing machine:
In our country, rotary type atmospheric pressure garment dyeing machine is widely used. This machine is made of stainless steel. In this machine, there are two big stainless steel cylinders one inside the other. The outer stainless steel cylinder is solid and have two sliding doors like microbus at the upper middle half position of the cylinder. The outer cylinder is fixed on the floor with heavy foundation to avoid any jerking during operation of the machine. There are also two chemical dosing doors on the sliding doors to facilitate chemical addition during machine running. The inner stainless steel cylinder is perforated having two stainless steel side shafts. The side shafts are fixed with the machine frame through ball bearing. Two machine pulley is fixed on the two side of the shafts. With the help of two big high power motor and motor pulley, the machine pulley is rotated. As a result, the inner perforated cylinder can rotate freely inside the outer cylinder. The perforated inner cylinder has also two spring loaded doors. The doors of the inner cylinder and outer cylinder is aligned to the same position by the use of a inching motion switch, to load and unload the garments to be dyed. The inner cylinder can be rotated at 5 to 35 rpm through control panel of the machine. The rotation of the inner cylinder is automatically controlled for clock-wise direction and anti-clock wise direction by reversal driving unit which is simple electronic circuit. The duel directional movement of the inner cylinder is used to avoid roping affect of the garments during dyeing.
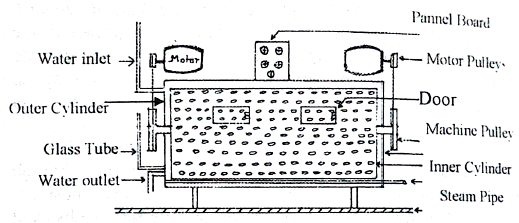
The inner cylinder is about 4 feet diameter and 6 feet wide. The exact size of the inner cylinder depends on machine capacity. There are three to four inches gap between the inner and outer cylinder. A solid steam pipe is situated between the gaps. Steam is supplied from the boiler through the steam pipe of the gap. Hence, liquor is indirectly heated by the steam pipe to use desired dyeing temperature of the dye liquor. Dyeing temperature is controlled by a dial and indicator situated in the panel board of the machine. Pre-set temperature of the dial and indicator automatically controls the liquor temperature by controlling the steam supply on-off through the steam pipe.
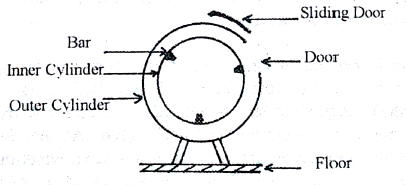
The inner cylinder has three triangular shape bars at equal distance that is 120 0 apart. The three triangular bars are about 6 inch high, which confirms the rotation of garments present inside the perforated cylinder during rotation of the perforated inner cylinder. Garments movement during garments dyeing is performed by those three bars which are also made of stainless steel.
The outer solid stainless steel cylinder has a connection through tube to a glass tube at the side of the cylinder at lower position. As a result height of the liquor in the machine can be observed during machine running. This tube helps to maintain liquor ratio before and during garments dyeing.
Form the over head water tank a water pipe connection is given to the bottom side of the outer cylinder with gate valve arrangement. So that, water can be loaded in the garments dyeing machine, simply by operating the gate valve. At the end of processing, liquor could be drained-out through two water out-let pipe fitted with gate valve. Simple operation of gate valve facilities easy out let of processed liquor from the garments dyeing machine.
There is another dial and pointer in the panel board which facilities pre-setting of processing time with alarm system. When the pre-set processing time of the dial reached, the machine automatically stops rotation with alarm sound to attract the attention of the operator for next operation.
The biggest advantage of this rotary garment dyeing machine is that the same machine can be used for desizing, scouring, bleaching. Dyeing and washing treatment of the garments. Capacity of garment dyeing machine may vary from 50 kg to 500 kg but the 300 kg capacity dyeing machine is mostly used in the garments dyeing industry.
2. High temperature rotary garments dyeing machine:
High temperature rotary garments dyeing machine is the modified and latest version of the atmospheric pressure type rotary garments dyeing machine. It is a microprocessor controlled high temperature garment dyeing machine which is not presently used in Bangladesh but it is used in the developed countries.
Garments dyeing could be carried out upto 1400C in this machine. Its main features are mentioned below:
- Very big central door facilities material loading and unloading mechanically.
- Light machine structure facilities high speed machine running with safe balance.
- Simple a/c drive and a/c converter facilities 5 to 35 rpm of main cylinder.
- Additional two chemicals tank facilities auto-dozing of dyes and chemicals during operation without any manual effort.
- Separate chemical dosing tanks may be attached besides those two chemicals dosing tanks for auto dozing of more number of items to the dye solution during operation or processing in that machine.
- Separate liquor circulating pump, heater and filter facilities additional liquor circulation, additional liquor heating and liquor filtration, hence better dyeing quality.
- The machine is available only built-in form hence less risk of installation and running problem.
It is a fully programmable automatic garment dyeing machine. In this machine all the dyeing parameters are to be pre-programmed in the monitor after loading the machine with the garments to be dyed. Important informations to be given input are, for example, processing time, processing temperature, processing speed, etc, which will be maintained by the machine automatically without any manual effort or even manual attention. In this machine upto 200 dyeing/pre-treatment program could be saved and re-used easily. The microprocessor can also be set for different question and answer about product and production parameters.
Basic Theory of Garment Dyeing:
Depending on wet fastness requirement of fabrics, garments made from cotton grey fabric are mainly dyed with direct dyes and reactive dyes. For low color fastness direct dyes are used and for high color fastness reactive dyes are used for cotton garments dyeing. If cotton garments are dyed with direct dyes then “hand wash separately” should be marked on the care label of the garments. If reactive dyes are used for cotton garments dyeing then the following advantages may be gained.
- Suitable for short and automatic dyeing process.
- Good level dyeing is achieved
- Dye migration and diffusion is better
- Color fastness is acceptable
- Total color range is available
If the cotton garments to be dyed with reactive dyes, then two types of reactive dyes are available in the market, namely
- Hot brand reactive dyes
- Cold brand reactive dyes
Among those two brands of reactive dyes, hot brand reactive dyes are commonly used for cotton garments dyeing. Because, cotton garments dyeing with hot brand reactive dyes facilitates easier and quicker dyeing process with reasonably good dyeing quality. Dyeing cycle for both brand of reactive dyes are discussed below.
1. Basic principle of garments dyeing with hot brand reactive dyes:
Cotton garments may be dyed with hot brand reactive dyes as per following line diagram of basic dyeing principle.

At first load hot water in the dye bath and add salt, lubricant, sequestering agent and maintain liquor pH at 7. Then load garments in the dye bath and start machine running. Raise liquor temperature of the dye bath to 80 degree Celsius with in 30 minutes. After 5 minutes at 800C, add dye solution in the dye bath within 15 minutes time. Continue dyeing for 30 minutes after dye addition in the liquor. Then add alkali to the dye liquor slowly within 15 minutes. After alkali addition, continue dyeing process for 30 to 60 minutes. At the end reduce liquor temperature to 700C and then drop the liquor.
After completion of dyeing, the garments are to be washed thoroughly at 400C to 450C for 5 minutes to remove the unfixed dyes from the garments fabric surface. Then drop the liquor. Again wash the garments only with normal water for 5 minutes to clean the garments again. At the end of dyeing cycle, softener may be applied on the garments to improve the softness property of the garments.
2. Basic principle of garments dyeing with cold brand reactive dyes:
Use of cold brand reactive dyes for cotton garmentw dyeing is less than the hot brand reactive dyes. Simply, possibility of irregular dyeing that is irregular shade formation is higher in case of cold brand reactive dyes. Basic dyeing principal of cold brand reactive dyes are discussed below:
Load the garments with required quantity of water and the garments to be dyed. Start machine running and add salt in the dye bath. Continue processing for 10 to 15 minutes. Then add dye solution in the liquor through chemical dosing door slowly within 20 minutes. Continue dyeing without temperature for next 60 to 90 minutes. Then add sodium carbonate to the dye liquor and continue treatment for 30 to 45 minutes.
After color shade matching, drop the dye liquor and use cold water wash to the dyed garments to remove unfixed dyes from the garment fabric surface. Drop the liquor and use light detergent wash on to the dyed garments to clean the garments. Drop the liquor and again use cold water wash to the dyed garments. After cleaning, unload the garments from the dyeing machine and dry the garments after hydroextruction.
Comparison of garments dyeing with hot and cold brand reactive dyes:
| Hot brand reactive dyes | Cold brand reactive dyes |
| Level dyeing may be achieved quickly. | Takes longer time to get level dyeing. |
| Exhaustion, reactivity, substantively and fixation property of hot brand dyes are better, hence quick level dyeing is achieved. | Needs careful control of dyeing process to achieve level dyeing. |
| Dye migration property of dyes are better, hence higher possibility of level dyeing. | Dye migration property of cold brand reactive dyes are poor, hence possibility of irregular dyeing exists. |
| The risk of irregular dyeing in the seam areas like pocket, flap, collar, cuff, etc. of garments is lower due to the effect of temperature. | The said risk is higher due to lack of temperature effect. |
| Normally dyeing is carried out between 800C to 950C. | Dyeing is carried out upto below 500C. |
| Entire dyeing process is easier and safer. | The process is little bit risky and needs always careful control. |
Special Chemicals for Garments Dyeing:
Use of special chemicals and dyes become essential for garments dyeing. Because the use of special chemicals and dyes facilities additional advantages as well as saves accessories from risk of damage present in the garments. For example, zipper used in the garment may be protected from corrosion during garments dyeing by the use of special chemicals.
Basically cotton garments are dyed in garments dyeing technique in our country. Cotton garments may be made from woven or knitted fabrics. Woven cotton garments dyeing process needs more precaution than the cotton knitted garments. Because, woven grey fabrics contains size materials and more impurities in the fabric than the cotton knitted fabrics. Use of metal components like zipper, button, stud, etc. is more in woven garments than the knitted garments. Possibility of crease marks formation during woven garments dyeing is more than the knitted garments.
Pretreatments of garments made from cotton grey fabrics prior to dyeing are very important because good pretreatment means half dyeing is completed. Normally pretreatment means Desizing; bacterial alpha amylase base Desizing agent provides better performance as because stability of enzyme activity is not affected by the variation of temperature and pH. normally at 70°c, ph 6- 7.5, 60 mins processing is enough for satisfactory Desizing. Use of high temperature reduces processing time. Use of nonionic wetting agent in the bath improves Desizing effect. Water hardness helps in stability of Desizing agents. Biolase, Bactosol, etc are the example of some of such Desizing agents.
After desizing of garments made from cotton grey fabric needs scouring and bleaching treatments to remove natural impurities present in the cotton fibers such as fats, waxes, pectins, pectose, ash, mineral organic compounds and coloring substances. During scouring and bleaching those impurities are removed from the cotton fibre. If those removed impurities forms insoluble compounds and suspended in the liquor, may redeposit on the garments fabric surface resulting color spot in the garment fabric after dyeing. To avoid such problem special chemicals like Sandopan LFW or sirrix A.K. liquid may be used.
Metal compound containing copper, iron, etc can destroy the bleaching performance. Presence of aluminum may be damaged by the action of the alkali. To avoid the problems of metals, during chemical treatment, Sandoclear 8160 or Sandopan SF liquid may be used. During bleaching of cotton/nylon blended fabric, nylon fiber may be damaged by the action of peroxide bleaching agent. If Lanalbin PA powder is used during peroxide bleaching then the nylon fibers will be unaffected by the bleaching agent. During hydrogen peroxide bleaching, stabilizer AWN of sandoze can be used which is better as stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide; moreover it has some detergency power and softness handle property.
To avoid the problem of crease marks formation during wet treatment, imacol brand as lubricant may be used in the chemical bath. Cotton fibers in garments form may be cataionised bysanden 8425 liquid @ 3% before garments dyeing to develop new color effect in the garments. During garments dyeing, some areas of the garments like collar, cuff, pocket and seam areas may be irregularly dyed due to interruption of dye penetration in those areas. To avoid the risk of irregular dyeing, leveling agent may be used in the bath. Drimagen E2R of clariant company if used in the dye bath, such types of problem can be avoided. Moreover it also sequester the calcium and magnesium ions if present in the dye bath. Before dye addition in the dye bath, use of 1 gram per litter drimagen E2R serves the purpose.
References:
- Garments Merchandising by Prof. M.A. Kashem
- Garment Manufacturing Technology Edited by Rajkishore Nayak and Rajiv Padhye
- https://textilelearner.blogspot.com/2011/03/description-of-garment-dyeing_6882.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dyeing
