Investigation on the Defects Found in the Different Types of Samples by Buyer in a RMG Industry
Authors:
Mosiur Rahman1
Hamid Hussain Azad
Dept. of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Email: mosiurrahman4315@gmail.com1
ABSTRACT
This project is on Investigation on the defects found in the different types of samples by buyer in a RMG industry. Sampling is important for a factory to show their work to get an order for bulk. If they can make sample in a proper quality and proper time and buyer will like their sample these can affect the factory economy to get an order.
Findings of the Project are Measurement problem, Print problem, Fitting problem, Fabric construction problem, sewing problem, Shade variation problem, Workmanship problem Different Kinds of defects in different types of samples. Causes, Impact and result of the problems; possible solutions of the problems. The goal of this project is to find out the Sample section dilemma and formulate possible as well as applicable solutions.
INTRODUCTION
1.1. Background of the Study
Sampling of garments is given great emphasis. It determines the approval of future orders from buyers and fetches business for a garment manufacturing or export company. Sampling is one of key elements of the pre-production processes in a garment industry. Before a manufacturer produces bulk orders, a prior sampling of styles is done to get approvals and jump start the fabrication of garments.
Sampling is not just for buyers, but the manufacturers can also derive estimates of yarn consumption for development of fabric, dyeing, printing, and stitching cost for a particular style or pattern given by the buyer. Companies can have a separate sampling department or a merchandiser, who works closely with the sampling section to source raw materials, and processes for developing a quality product for an affordable price.
Sampling includes details like a product/style code or a reference number, color specifications, kind of fabric, composition, description, quantity, and details of embroidery, buttons, zippers, or any other sort of accessories used. Hence it can be said that various types of samples of garments work as a bridge between buyers and the producers.
There are many people who are involved directly and indirectly in the process of sampling. Designers, buyers, individuals engaged in sourcing and purchasing, production team, quality control personnel, and the costing department at different levels work closely on the sampling of garments.
There are various types of samples that are developed by manufacturers depending on the requirement of their respective buyers. The following is a list of different types of samples used in the garment export industry:
1.2 Objectives of the study:
The followings are the main objectives of the present study:
- To know about sample making system and their types.
- To find out the reasons of sample failure.
- How to prevent these problems.
- To know about the garments sampling failure reason.
- To know about buyers requirement types of samples.
1.3 Limitations of the Study
Several levels of officers, employees helped us in several conditions. Though, we have faced a few problems, which I should mention to depend on the research.
The followings are some problems:
- We have not much knowledge about it. We have to gather.
- It is not possible to learn about sample making and find out their failure problem within 60 days.
- We have not got old & extra documents.
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 History of garments industry in Bangladesh
The foundation of textile sector was first established in the 60th decade of 19th century. For the first time, the industry exported shirts (Mercury shirt) to the European market in 1965-66, which was produced from Karachi. In the latter, 9 exporting industries were available in 1977-78. The three largest industries in that time were Riaz Garments, Jewel Garments and Paris Garments. Among those, Riaz Garments was the most famous and oldest industry in that time.
In the earlier stage, Riaz Garments of Mohammad Reaz Uddin started its business with some tailoring shop in the name of Riaz store. In the later, the name turned into Riaz Garments from Riaz store in 1973 and from 1978 the company started exporting products in the abroad by exporting 1 million pieces of shirts in the South Korean Company named “Olanda”. “Desh Garments” is another pioneer of Bangladesh RMG sector. In 1979, Desh Garments started a joint project with South Korean company “Daiyuu”.
At the same time, several garments were introduced such as-Style craft limited by Shamsur Rahman, Aristo craft Limited by AM Subid Ali, Azim Group by Engineer Mohammad Fazlul Azim and Sunman Group by Major (Retd) Abdul Mannan.
By following the beginners of RMG sector, some others discreet and hard-working entrepreneurs started their RMG business in the country. From there, RMG sector of Bangladesh was developing day by day and not needed to look back. Though this sector had passed various critical stages through the path. In that time, we learned about child labor 1994 and in 1995 we made our garments industry free from child labor very successfully
2.2 Overview of Bangladesh RMG Industry
The ready-made garments (RMG) sector of Bangladesh has got a greater facet than any other sector in terms of growth and foreign exchange earnings. It makes a significant contribution to the national economy by creating generous employment opportunities and reducing poverty through socioeconomic development. Despite unquestionable success story, this sector has got a number of formidable challenges for the future growth. The present study has made a search on different dimensions of contribution and challenges of RMG industry in Bangladesh. To accomplish the task, a descriptive research based on study of available records is conducted. The study reveals that since its inception, especially during the last three decades, the RMG industry contributed significantly through creation of physical infrastructure which is demonstrated by 4222 RMG units along with the development of human capital as around 4 million workforce are directly involved in this industry. It has also contributed tremendously through empowering women as almost 90 percent of its labour force is female which ranked the highest in South-East Asia. In terms of core economic consideration RMG holds almost 14.07 percent of the GDP of Bangladesh as well as the 81% of the total export earnings. The study however, identifies some challenges towards its future development including unskilled workers, improper infrastructure, energy crisis, bank loan and high rate of interest, high tax rate, intricate social compliance, political crisis, lack of market and product diversification, compliance pressure of accord and alliance and lack of integration.
The RMG sector of Bangladesh as employing the rural poor illiterate female workers is known for cheap labour and also producing low value garments. So producing high value products remains a challenge for it. Besides, there is a high dependency on imported raw materials especially in case of woven garments that cause high lead time in production. Thus, this industry is established for low value apparels products at low price. There are very less interest in developing technical skill, training and innovation, research and development activities within the sector to develop it and transform to high pay- high value products. That ultimately reduces the competitiveness this sector in the long run. In addition, there exists monotony for repetitive work, low motivation in the workplace. Frequent political violence, natural disaster or act of God often disrupts unrest and affect at the RMG sector. For example, an export order of US$15,000 million could not meet on time due to the flood of 1998, and more than 3 lakh workers were victims of the flood (Kuddus & Rashid, 1999). Besides, there has been several life causing accidents such as Rana Plaza and Tazrin events that brought the workplace safety in the limelight as the most pressing challenge for the RMG sector. Apart from the government initiatives, global brands and retailers have taken major initiatives through creation of the Bangladesh Accord on Fire and Building Safety ‘Accord’ and the Alliance for Bangladesh Worker Safety ‘Alliance’. Apart from the internal challenges, the RMG sector also suffers from the challenge of world political and economic order. For example, recent devaluation of EURO against USD has created a spot of botherfor the RMG sector. It makes the Bangladesh RMG product expensive in EU market which is the major export zone for Bangladesh. Political crisis such as terrorist attack in USA in 2001 and followed by a depression in 2004 caused a decline in Bangladesh export to USA by 13.04 percent (Abdin, 2008). In spite of its contribution into the economy in terms of employment and income generation, this sector is also facing some challenges from inside and outside.
2.3 Development and progression of Bangladesh RMG Industry
According tothe data of Export Promotion Bureau (EPB), the apparel sector, employer of 4 million workers, has contributed 84.21% to Bangladesh’s total exports of $40.53 billion.
In the FY19, Bangladesh’s export earnings from the RMG sector stood at $34.13 billion, posting 11.49% growth. In the fiscal year 2017-18, apparel sector earned $30.61 billion & the growth was 8.76%, thanks to workplace safety improvement.
In the FY19, apparel sector exceeded the export target by 4.42%. Bangladesh has set a target to earn $32.68 billion.
Of the total amount, Knitwear products fetched $16.88 billion, which is 11.19% higher than the $15.18 billion in the same period a year ago. Woven products earned $17.24 billion, up by 11.79%, compared to $15.42 billion a year ago.
The specialized textile sector saw a 28.51% growth to $144 million, while the home textile sector saw negative growth in earnings by 3.07% to $851.72 million, which was $878.68 million.
Meanwhile, Bangladesh’s overall export earnings have registered a 10.55% growth to $40.53 billion in the just-concluded fiscal year.
2.4. Definition of sample
Garment sampling is very much important process. It is a model of what the bulk production is going to be done. Sample is the reference garments corresponds to-
There may be a separate sampling department in a company. But as the merchandiser is the person who is interacting with the buyers regarding samples and other requirements, this sampling department will work under the guidance.
2.5. Purpose of Sample
- Getting clarifications about style details from the merchandiser,
- Checking Pattern’s work-ability,
- Preparation of different types of samples and getting the buyer’s approval,
- Informing quality related problems, encountered during preparing samples to QC,
- Minimizing operations and consumption.
2.6. Process flow chart of garments sample making
Garments sample play an important role for receiving a garments export order. Sample section of garments manufacturing factory has done this job. As a result, among all the others section like as cutting, sewing, finishing etc. sample section gets the maximum priority in demands. A garment merchandiser should have excellent idea about the process flow chart of sample making which will help him to facilitate the other duties of a garments export order.
Received tech pack from the buyer
↓
↓
Fabric cutting
↓
Print or embroidery (if required)
↓
Sewing
↓
Finishing
↓
QC check
↓
Send to the buyer for approval
2.7. Types of samples & uses:
| Serial no. | Sample | Use |
| 01 | Proto/ Development Sample | To convert the pattern into actual garment. |
| 02 | Size set/ Grade/ Fitting Sample | To fit the styling of the garment. |
| 03 | Additional Sample (White Only) Magazine. Photo shot) garment on the rack. | All these types of samples are made to show the garment of the rack |
| 04 | Contract Seal/ Seal Sample | To gain approval before the bulk Production. |
| 05 | Pre-Production (PP) sample | To gain approval before the bulk Production. |
| 06 | Production Sample | To gain approval for shipping the garment._ |
| 07 | Sales Man Sample (SMS) | To gain approval for bulk production |
Table 2.1: Types of samples & their uses.
2.8. Types of Samples Required for Completing a Garments Order
There are mainly eight types of samples needed for completing a garment order. Those Ares-
- Fit sample,
- Proto sample,
- Size set sample,
- Counter sample,
- Salesman sample (SMS),
- Pre-production sample (PPS),
- Top over production sample (TOP),
- Shipment sample.
2.9. Sample Development in Garment Industry
Process Flow Chart of Sample Development in Garment Industry
Program Received from Buyer
↓
Personal Study on Tech pack
↓
Meeting with Internal Team
↓
Advice for pattern making
↓
Sourcing Raw materials
↓
After Receiving Raw Materials Send to Sample Section
↓
Cutting
↓
Printing/Artwork
↓
Sewing
↓
Washing (If Needed)
↓
Finishing and QC
↓
Final Review
↓
Tagging
↓
Packing/Invoice
↓
Send to Buyer
METHODOLOGY
3.1. The buyers whose sample garments order report we had studied:
- H&M
- VARNER
- GU
- NEXT
3.2 Data Collection:
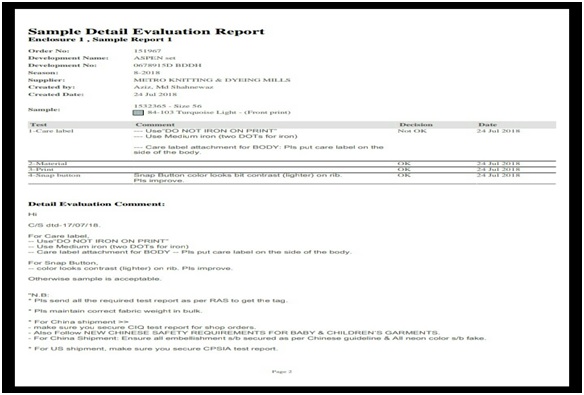



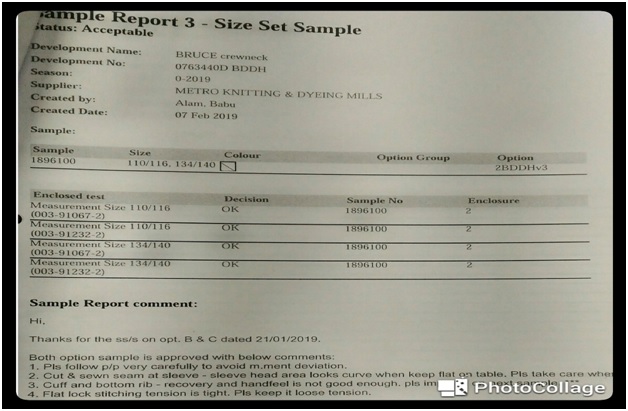
3.3 The number of the report analysis
| S.L | Buyer name | Name of the Problem | |||||||
| No | Measurement problem | Sewing problem | Fitting problem | Shade variation & dyeing problem | Print problem | Workmansip problem | Fabric construction problem | Access. prob | |
| 1 |
H&M
| Y | Y | Y | |||||
| 2 | Y | Y | Y | ||||||
| 3 | Y | ||||||||
| 4 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| 5 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| 6 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| 7 | Y | ||||||||
| 8 | Y | Y | |||||||
| 9 | H&M | Y | Y | ||||||
| 10 | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||
| 11 | GU | Y | Y | ||||||
| 12 | Y | Y | Y | ||||||
| 13 | NEXT | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||
| 14 | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||
| 15 | TEZENIS
| Y | |||||||
| 16 | Y | ||||||||
| 17 | VARNER
| Y | Y | Y | |||||
| 18 | Y | Y | |||||||
| 19 | Y | ||||||||
| 20 | Y | Y | |||||||
| 21 | Y | Y | Y | ||||||
| Total Defects | 11 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 5 | 10 | |
| Total% | 20% | 9.09% | 10.90% | 9.09% | 7.27% | 16.36% | 9.09% | 18.18% | |
Table 3.1: The number of the report analysis
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1. Discussion
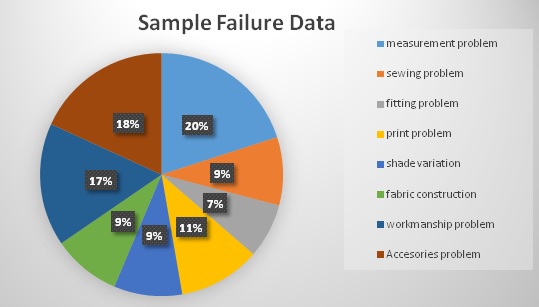
In sample section we saw how a sample made and how buyers comment on it. We saw various comments on sample and how many problems occurred during sampling. There are many problems in sampling like measurement problem, sewing defects, print problem, shade variation, accessories problem, workmanship problem, fabric construction problem etc. Above all this measurement problem is main problem according to our research. For this many sample are failed. So pattern department should work more carefully and QC should be more careful about it.
4.2. Fail percentage of the sample garments
- Measurement problem (20%)
- Sewing problem (09%))
- Print problem (90%)
- Fitting problem (27%)
- Fabric construction problem (09 %%)
- Workmanship problem (36%)
- Shade variation & Dyeing problem (09 %%)
- Accessories problem (18.18%)
4.3. Reason for the sample failure
| SL. No. | Reason | No. of sample failed |
| 1 | Measurement problem | 11 |
| 2 | Sewing problem | 5 |
| 3 | Print problem | 4 |
| 4 | Fitting problem | 6 |
| 5 | Fabric construction problem | 5 |
| 6 | Workmanship problem | 9 |
| 7 | Shade variation & Dyeing problem | 5 |
| 8 | Accessories problem | 10 |
| Total | 55 |
Table 4.1: Reason for the sample failure
4.4. Graphical view of sample failure data
4.5. Major problems with their Remedies
Now we will discuss about these problems and their remedies:-
4.5.1. Measurement problem (20%):
Definition:
Measurement problem can be defined as when the workers can’t match the measurement with buyer. They make some silly mistake on measurement.
Sketch:
 Causes of measurement problem:
Causes of measurement problem:
- Lack of inspection of given measurement.
- For shrinkage measurement problem occurs.
Remedies of Measurement problem:
- Measurements check properly
- Should check the Front Part, Back part, Sleeve properly.
- Let the fabric relax for proper time, before cutting. .
4.5.2. Sewing problem (9.09%):
Definition:
The problem can be defined when the seam line is not proper it is called sewing problem. as the improper application of a series of stitches.
Sketch:
 Causes of sewing problem:
Causes of sewing problem:
- Skipped stitches
- Unbalance stitch
- Staggered stitch
- Seam Puckering
- Bobbin or looper thread breakage,
- Needle thread breakage
- Thread fusing when sewing machine stops.
Remedies of sewing problems:
- Proper placement of looper needle or hook
- Needle size and thread size to be altered
- Stitching fault should be checked
- Seam fault check
- Correct placement of interlining
- Proper winding of threads on to the bobbin
- Setting proper tension to the sewing thread
4.5.3. Print problem (10.90%):
Definition:
The problem that is caused by not coloration in the proper area and proper colour, proper shade is called print problem.
Causes and Remedies of Printing Defects:
Misfit or Out of Registration: A misfit is a defect caused when screens are not properly aligned. The misaligned screens can leave an area unprinted or cause the pattern overlapon oneanother.
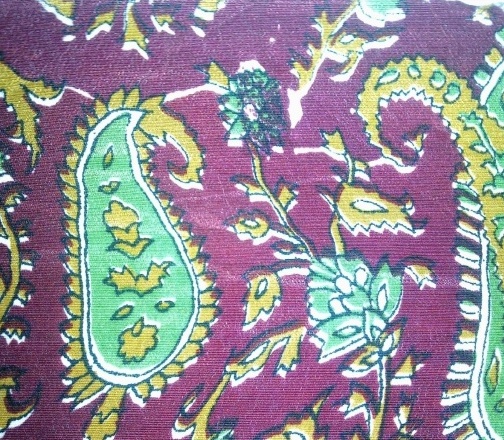

Stick-in: A stick-in occurs when a small fiber or yarn get stuck in one of the screen openings. It can result is a small unprinted circle in the design of the size of the tip of a pen. A stick-in is very difficult to see and often go unnoticed.

Blurred patch: unwanted blotch or bar in a printed dyed/fabric results in a blurred patch.
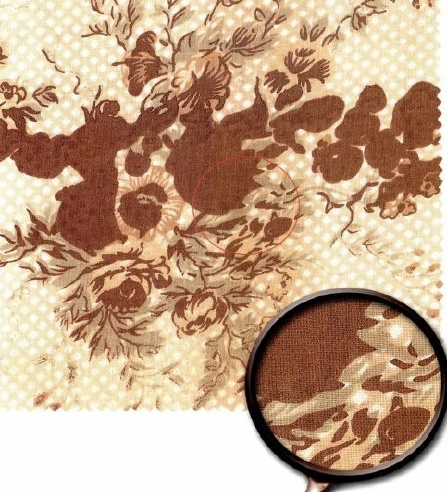

Tinting: In a printing fabric the design at one place is bold as required; while at other place the same is hazy, light and unclear.
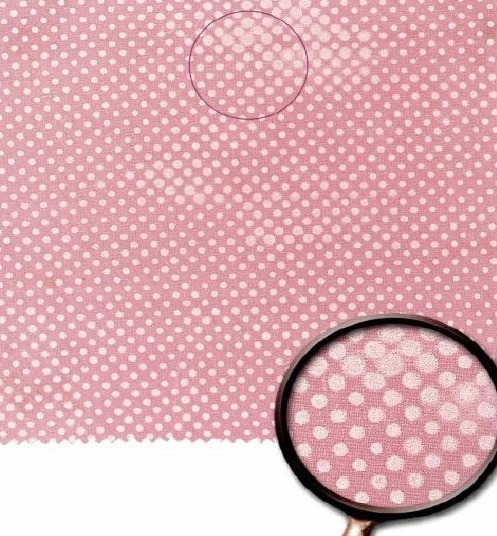

Bleeding: Causes due to low viscosity of print paste .It is major defect as it happens throughout the fabric unless the viscosity is corrected.

Misprint or no print on selvedge: Improper setting, defective guiders, and uneven width of the fabric at stitches are the reasons for misprint on selvedge.
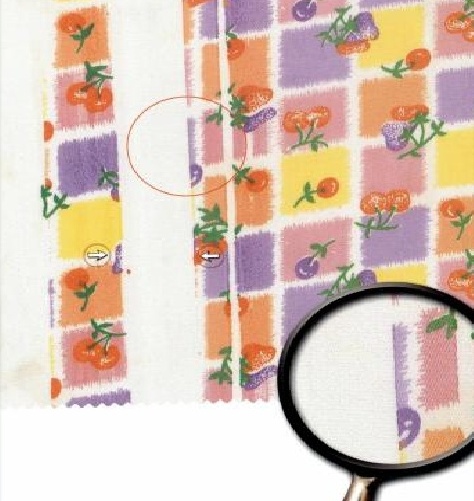

Colour out: While printing, if the colour paste runs low in the reservoir resulting in blank skips in the print pattern it is called as Colour out. Continuous monitoring of the level of the colour pastes can overcome this problem.
4.5.4. Fitting problem (13.33%):
Definition:
Fitting problem is the not proper adjustment of different parts of the garments when it is wear on a dummy or a person. Sometimes it is more loose or sometimes it is more tight to wear that’s the problem.
Causes of fitting problem:
- Due to fabric shrinkage
- Due to improper measurement
Remedies of fitting problem:
- Proper measurement
- Fabric shrinkage testing
- Should Proper careful during sewing
4.5.5. Fabric construction problem (9.09%):
Definition:
We faces different problem in the fabric construction like GSM problem, needle mark, patta.
Causes:
- For lack of inspection properly
- Machine problem or needle problem
Remedies:
- Should inspection properly
- Check the machine before production
4.5.6. Workmanship problem (16.36%):
Definition:
Workmanship problem can be defined as all problems that are done by the workers.
Causes:
- due to less concentration on work
- due to Lack of proper training
- Due to Less inspection of supervisor.
Remedies of workmanship problem:
- Proper concentration on work.
- Need proper training.
- Proper inspection on their work
4.5.7. Shade variation & dyeing problem (9.09%):
Sketch:

Causes of shade variation dyeing defects:
- Uneven pre-treatment (uneven scouring and bleaching).
- Improper colour dosing.
- Using dyes of high fixation property.
- Final cationic softener treatment.
- PH, reel speed, dye are a main thing to causes shade variation.
Remedies of shade variation problem:
- Scouring and bleaching should be done properly
- Colour dosing should be done properly.
- Should maintain the process parameters i.e. time, temperature and speed carefully.
4.5.8. Accessories problem (18.18%)
Definition:
When accessories and trimmings are not as expected pieces and not proper quality
That’s the problem occurred.
Causes:
- Button colornot matching with Techpac
- Sometimes care label missing or not attached in the right position.
- The elastic is not latex free
- Lack of right direction in the care label
- Not using a grade polybag.
CONCLUSION
Sample making is very important in the garment manufacturing process. Everything is depends on the making of sample or the quality of sample. For making good quality sample we need good artwork, fabric, accessories, good merchandiser who take it good care and proper follow up. We work on sample comments from buyer. We saw that majority problem is the measurement problem. It is occurred due to pattern problem. We need to overcome this problem. We have to follow the measurement chart properly. If we overcome this we will face less problem. Our sample will best quality full sample and we can save our time, we will get production order early.
References:
- Information gathered from METRO KNITTING AND DYEING LTD.
- Garments Technology by Prof. M. A. Kashem
- Garment Manufacturing Technology by Md. Shafiul Azam, Md. Abu Saleh & Khondokar Abu Nafiz
- https://garmentsmerchandising.com/types-of-samples-required-for-garments-export-order
- https://textileapex.blogspot.com/2014/10/sample-html

 Causes of measurement problem:
Causes of measurement problem: Causes of sewing problem:
Causes of sewing problem: