Principal Classes of Synthetic Dyes and Their Characteristics
Muhammad Ali Uddin Alvi
Department of Textile Engineering,
Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro, Pakistan
Email: alialvi.textile@gmail.com
Synthetic Dyes in Textile:
Synthetic dyes are derived from organic or inorganic compounds. These synthetic dyes have harmful effects on the environment and human beings. Synthetic dyes are sometimes referred to as ‘coal tar dyes’, since they are manufactured from substances which, until recently, were only obtained from coal tar. Though it is harmful for human being and environment but synthetic dyes are playing important roles in our modern life with applications in both industry and scientific laboratories. Synthetic dyes are widely used in the field of textile, paint, and printing. Acid dye, basic dye, reactive dye, direct dye, sulfur dye, disperse dye are example of synthetic dyes. In this article I will classify synthetic dyes and give important characteristics of these synthetic dyes.

Characteristics of Acid Dye:
- General Description: Originated from basic dye acidification; complete color range.
- Uses: Primarily for wool and silk; also acetate, acrylic, nylon.
- Ionic nature: Anionic
- Light fastness: Very good
- Washing fastness: Poor
- Hot pressing fastness: Not affected
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Fair
- Perspiration fastness: Fair
- Crocking fastness: Excellent
- Solubility: Soluble in water
- Molecular Size: Average
- Substantivity: Low to moderate
- Application pH: 4-5
- Shades: Complete color range
- Types: 1. SDC class A: good leveling, 2. SDC class B: average leveling, 3. SDC class C: Poor levelling
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Acid Dye:
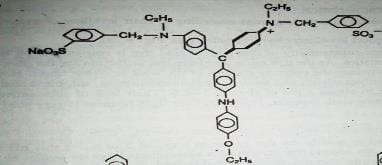
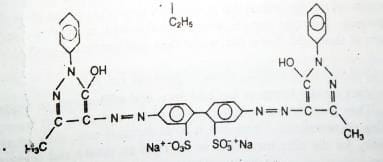
Characteristics of Basic Dye:
- General Description: First synthetic dye (1856), first coal-tar dye was a so called basic dye
- Uses: Primarily for wool, silk, nylon, cotton (with mordant)
- Ionic nature: Cationic
- Light fastness: Poor
- Washing fastness: Poor on natural fibers good on others
- Hot pressing fastness: Not affected
- Dry cleaning fastness: Mostly poor
- Sea water fastness: Very poor
- Perspiration fastness: Poor
- Crocking fastness: Good resistance on acrylics
- Solubility: Soluble
- Molecular Size: Average
- Substantivity: Low to moderate
- Application pH: 5-6
- Shades: Complete color range: bright colors
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Basic Dye:
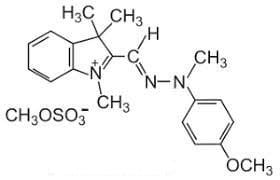
You may also like: Various Classification of Dyes | Different Types of Dyes
Characteristics of Direct Dye:
- General Description: Dye cellulosics directly; some dye wool, silk.
- Uses: Primarily for cellulosic fabrics (without mordant)
- Ionic nature: Anionic
- Light fastness: Good to excellent
- Washing fastness: Poor
- Hot pressing fastness: Good
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Poor to good depending on color
- Perspiration fastness: Good
- Crocking fastness: Very good
- Solubility: Depends on types of direct dyes
- Molecular Size: Very large size in anionic dyes
- Substantivity: Depends on types of direct dyes
- Application pH: 7
- Shades: Complete shade range
- Types: 1. SDC class A: self levelling , 2. SDC class B: salt controllable, 3. SDC class C: very salt sensitive
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Direct Dye:
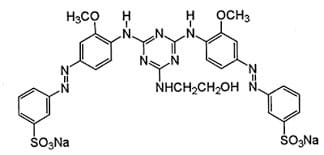
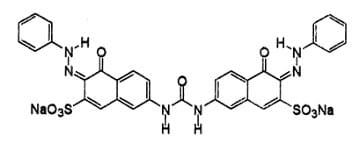
Characteristics of Disperse Dye:
- General Description: Developed for acetate. In soluble in water.
- Uses: Primarily for acetate, also polyester, nylon, cellulose fibers.
- Ionic nature: Non-ionic
- Light fastness: Fair to excellent depending on fiber
- Washing fastness: Fair to good
- Hot pressing fastness: Some color change possible
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Good
- Perspiration fastness: Good
- Crocking fastness: Good
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water
- Molecular Size: Very small
- Substantivity: Low
- Application pH: 4-5
- Shades: Good shade range
- Types: 1. High energy level, 2. Medium energy level, 3. Low energy level
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Disperse Dye:
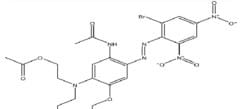
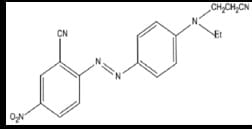
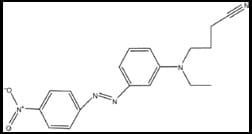
Characteristics of Reactive Dye:
- General Description: Form covalent bond with fiber
- Uses: Primarily for cotton apparel
- Ionic nature: Anionic
- Light fastness: Very good
- Washing fastness: Good
- Hot pressing fastness: Not affected
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Good; some fair, in chlorinated pool
- Perspiration fastness: Good
- Crocking fastness: Good
- Solubility: Depends on types of reactive dyes.
- Molecular Size: Average & linear
- Substantivity: Depends on types of reactive dyes.
- Application pH: 11 to 13
- Shades: Brightest shade on cotton
- Types: 1. SDC class A: Low reactive, 2. SDC class B: Medium reactive, 3. SDC class C: High reactive
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Reactive Dye:
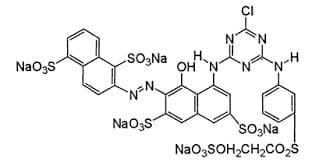
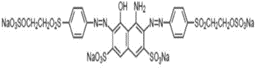
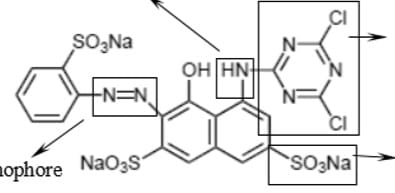
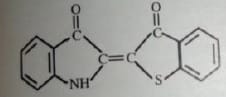
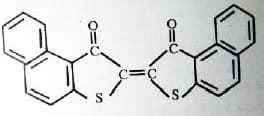
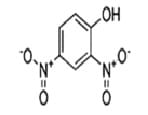
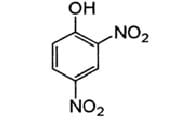
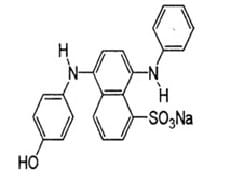
Characteristics of Sulfur Dye:
- General Description: Insoluble in water, complete shade range
- Uses: Used for linen, cotton, jute
- Ionic nature: Non-ionic
- Light fastness: Poor to fair for yellow and brown, good to excellent in darker shades
- Washing fastness: Poor to good
- Hot pressing fastness: Good
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Good
- Perspiration fastness: Good
- Crocking fastness: Poor to good
- Solubility: Insoluble
- Molecular Size: Very large size in nonionic dyes
- Substantivity: Low substantive, before reduction
- Application pH: 10 to 11
- Shades: Complete shade range except true red, colors not bright
- Types: 1. Water insoluble dyes, 2. Leuco Sulphur dyes, 3. Solubilised Sulphur dyes.
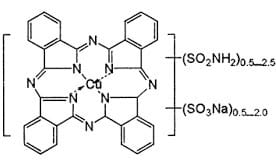
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Sulfur Dye:
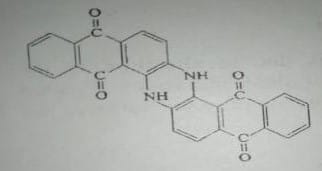
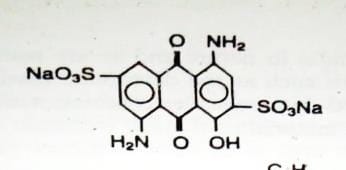
Characteristics of Vat Dye:
- General Description: Synthetic indigo original
- Uses: Used for cotton, wool
- Ionic nature: Non-ionic
- Light fastness: Excellent
- Washing fastness: Good
- Hot pressing fastness: Good
- Dry cleaning fastness: Good
- Sea water fastness: Good
- Perspiration fastness: Good
- Crocking fastness: Fair to good
- Solubility: Insoluble, soluble leuco salts
- Molecular Size: Very large
- Substantivity: Depends on types of vat dyes
- Application pH: 12 to 13
- Shades: Incomplete but adequate shade range (dull colors)
- Types: 1. SDC class A: (indigoid), 2. SDC class B: (thio indigoid), 3. SDC class C: Anthraquinonoid
You may also like: Different Types of Dyeing Methods
Example Dye Structure / Color Index of Vat Dye: