What is Quality?
Quality is all the features in the product to meet customer requirements. Quality is a multifaceted concept that describes how well a service, process, material, or product possesses desired intangible or physical attributes.
Quality Management:
- The act of overseeing all activities and tasks needed to maintain a desired level of excellence.
- This includes creating and implementing quality planning and assurance, as well as quality control and quality improvement.
Quality Management Components:
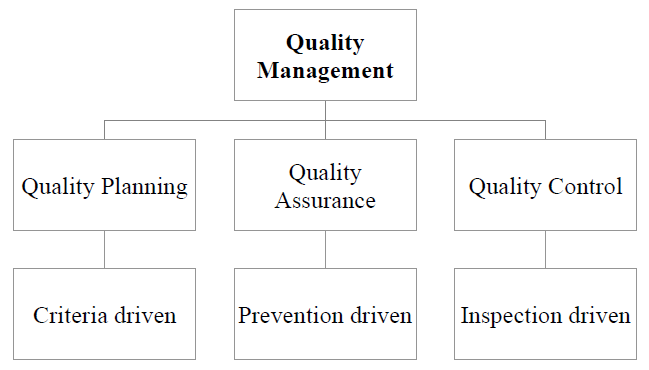
Components of quality management are described below:
Quality Planning- Criteria Driven
- It identifies the standards and determines how to satisfy those standards.
- It lays out the roles and responsibilities, resources, procedures, and processes to be utilized for quality control and quality assurance.
Quality Assurance- Prevention driven
- It is the review to ensure aligning with the quality standards.
- Planned and systematic quality activities.
- Provide the confidence that the standards will be met.
Quality Control- Inspection driven
- It addresses the assessment conducted during Quality Assurance for corrective actions.
- Measure specific results to determine that they match the standards.
- Use of Statistical Process Control (SPC) for monitoring a process to identify special causes of variation and signal the need to take corrective action when appropriate.
Dimensions of Quality:
The quality of a product or service is assessed based on some parameters which are termed as the dimension of quality.
- Performance
- Durability
- Aesthetics
- Features
- Serviceability
- Conformance
- Reliability
- Perceived quality.
Quality Control:
Quality control is a continuous and regular control of the parameters which affect the quality of the final product. Quality assurance is the “process of designing, producing, evaluating, and assessing products to determine that they meet the desired quality level for a company’s target market”. Quality control is generally understood as assessing for quality after products have already been manufactured and sorted into acceptable and unacceptable categories. It is costly for companies that do not take a quality assurance method, but only look at quality in terms of quality control.
Quality Control in Apparel Industry:
It comprises of planning, raw data compilation, its investigation and implementation. In the process of quality control, the control at various levels of production of garments is monitored by various control forms. This helps in maintaining continuity in the quality control. Further monitoring of the production process will be controlled by documentation. The stage-by-stage documentation helps in not only achieving the expected quality but also in completion of production within the target time.

Quality control is the day-to-day implementation of quality assurance, and to succeed you have to be very proactive at all levels. Quality controllers need to learn as much as they can about all aspects of the business as they will need to liaise with all departments in the company as well as customers and suppliers.
Investment in quality control is a form of insurance, but it does not wait for disaster to happen then compensates you; it works to prevent the disaster from happening in the first place. If implemented properly, it is continuously maintaining, servicing, and repairing your supply chain.
Quality control in apparel industry can be executed through classifying the entire industry into following sub-divisions:
- Pre-production stages
- Production stages
- Post-production stages.
1. Quality control in Pre-production:
a) Fabric quality control through assessing:
- Comfort properties
- Colorfastness properties
- Durability properties
- Other technical properties such as GSM, carded/combed yarn, composition, EPI, PPI, etc.
b) Other trimmings and accessories such as:
- Closure
- Zipper, Button, Hooks, Snap fasteners, Drawstrings, etc.
- Interlinings/interfacing
- Sewing threads
- Elastic waistband
- Other design elements such as:
- Beads, Sequins, Braids, Fringes etc.
2. Quality control in Production:
- QC in Spreading
- QC in cutting
- QC in assembling parts
- QC in sewing
- QC in finishing.
3. Quality control in Post-Production/Final inspection:
- Technical parameters such as:
- Defects in yarn, fabrics.
- Defects in trims and accessories.
- Stitching defects.
- Seam defects etc.
- Performances such as:
- Overall appearance.
- Sizing and fit.
Note:
Digital supply chain solutions, like QUONDA by Triple Tree, can help apparel brands streamline quality inspections and detect defects early on in the process. The application digitizes an otherwise manual and labor-intensive process and reduces the risk of human error. With computer vision technology and smart e-tape integration, measurements are quicker and more accurate.
Additionally, QUONDA’s data-driven insights help brands make more informed decisions. Areas for improvement can be identified and proactive measures can be taken to cut down on defects much earlier in the production process, saving time and money, while increasing efficiency.
You may also like:
- Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) in Apparel Industry
- Study on Quality Control in Sewing Section
- Basic Concepts of Quality and Quality Control in Textile
