What is Geotextile?
Geotextiles are permeable textile materials and can be woven, nonwoven, or knitted. It’s a member of a larger family called Geosynthetics. Geotextile is one of the first textile products in the human history. It’s played a significant part in modern engineering design and maintenance techniques.
Every textiles product applied under the soil is a geotextile. The word ‘geotextile’ is a modern manufacturing process to trace their origins to traditional textile manufacturing techniques. Geotextile can be newly emerged field in the Civil Engineering.
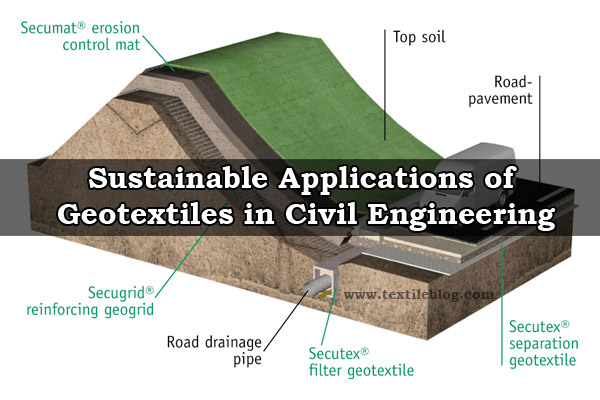
The first textiles that were used in civil engineering projects were placed in soil for landscaping and building construction projects to stabilize and reinforce the soil. It has been used very successfully in road construction for over 30 years.
In the early 1970s new raw materials specifically adapted for the manufacture of technical textiles for use in civil engineering works. Now, sustainable geotextile could be a specialized technologically sophisticated industry.
Functions of Geotextile:
The mode of operation of a geotextile may be defined by six discrete functions:
- Filtration
- Separation
- Drainage
- Reinforcement
- Sealing and Protection.
Relationship between manufacturing process and functions of geotextiles:
| Filtration | Nonwoven: Needle punch technique and use of a mix of fibres of different dimensions makes it possible to control pore size openings with great precision. It gives non-woven geotextiles an advantage over other products. Woven: Openings are often very large but very even. This product can thus lend itself to precise applications such a nonclothing filter. Knitted: Evenness of knitted geotextile makes it possible to control openings perfectly. It’s the ability to obtain very fine openings that are ideal for filtration of sandy or salty soils. The ability to stretch and the round form that can obtain by certain knitting procedures make this product an economical solution for use around perforated drainage pipes. |
| Separation | Nonwoven: The openings lofty structure of nonwoven needle punched geotextiles gives them the capacity to manage water well, as well as fine particles in the soil. It providing efficient mechanical separation owing to resistance to mechanical forces, which can strong. Slit Film: The high elongation modulus of woven slit film geotextiles lends itself to combining two functions that often coexist in road engineering applications to separation and reinforcement. |
| Drainage | Nonwoven: Needle punch makes it possible to obtain an open and lofty structure. Offering thickness and permeability needed for drainage functions. Nonwoven needle punched geotextiles are used combined with other fibres and materials to increase drainage capacity. |
| Reinforcement | Slit Film: Among the most used reinforcement solutions, owing to their low elongation and high tensile strength, relative to their thickness and weight. Monofilaments: Woven high-tenacity monofilament geotextiles are developed and are well-suited for reinforcement functions owing to their excellent tensile strength. Knitted: It is used for applications where extreme reinforcement is needed. It offers significantly low elongation and high tensile strength versus thickness or weight. |
| Protection | Nonwoven: Needle punch method allows tighter binding and entangling of the fibres, offering a cohesive, puncture-resistant structure. |
| Liquid barrier | The open structure of nonwoven geotextiles allows itself to be soaked with combined with clay particles that enter open spaces within the structure of the geotextile to prohibit the passage of liquids. |
Table: Relationship between manufacturing process and functions of geotextiles
Functional properties of geotextiles:
| Characteristics of Geotextile | Properties |
| Physical properties: |
|
| Mechanical properties:
|
|
| Hydraulic properties: |
|
| Degradation properties:
|
|
Sustainable Applications of Geotextiles in Civil Engineering
Sustainability is a widely used term that have many different meanings. But for geotextile, ‘sustainable application’ is common term that diversified the technical textile as well as geotextile field. Geotextiles are sustainable ideal materials for infrastructural. Recently it has been used and evaluated for modern civil engineering construction.
Geotextiles are technical fabrics used in civil engineering construction projects such as road pavements, railway track, dams, river canals and costal work, embankments, drainage, and silt fencing for the purpose of soil reinforcement and stabilization, sport field construction, sedimentation and erosion control, agricultural and many sustainable other applications.
Sustainable geotextiles are affecting construction in civil engineering practice. Geotextile applied in civil engineering are helping make the world sustainable for mankind.
Civil engineering works where geotextiles are applied, it may be classified into the following categories:
- Road Works
- Railway Works
- Embankments protection
- Soil Erosion
- Drainage
- Agriculture
- Aquaculture
- Commercial development, etc.
Above all points are described briefly:
1. Road Works:
Geotextiles are used as reinforcement in paved and unpaved roads to improve construction and long-term sustainable performance. The reinforcement sustainable function of geotextiles requires separation of the aggregate from the subgrade soil and filtration to be allowed water to pass freely from weak, wet sub grade soil into the aggregate layer owing to excess pore water pressure during, for optimal improvement in roadway performance.
2. Railway Works:
Improvements are accomplished through structural interaction with granular layers in the railway works, enhancing the integrity and structural capacity of these support layers over the life of the system. The geo fabrics used to separate the soil from the sub-soil without impeding averting the ground water circulation. Each layer of sustainable geomaterials prevents wandering off sideways because of shocking and vibrations from running trains.
3. Embankments protection:
The sustainable protection of the river and canals banks, seashore, coastal works, and embankments flexibility, permeability, and increase the ability to cross-flow of water makes natural geotextiles a standard material to protect. The sustainable circumstances of natural geotextiles on eco system are important wherever slopes to protect in contacting with water.
4. Soil Erosion:
Geological soil erosions are caused by the action of wind and rain, rivers and oceans on undisturbed soils. Erosion control is the most important major growing area for the applications of geotextiles in civil engineering. Geotextiles protect river banks from erosion due to currents.
5. Drainage:
Geotextiles have been used successfully as drainage materials in geo-technical and geo-environmental engineering for the last 40 years. It has been used in the leakage and gas collection systems of landfills. It sustainable to the filter mechanism for drainages in dams, roads, railway track, drainage trenches and agriculture works also.
6. Agriculture:
Geotextiles are widely used in sustainable farmland for cultivating. Cold temperatures, typhoons, strong wind, strong sun exposure, the impact of rain, insects, and weeds are major challenges for agricultural production in many countries. Freezing and frost, wind, and sun protection, insect protection, ground covering for weed control, shading treatment for flower induction, storage and freshness protection, and fruit and vegetable package materials is major applications of sustainable geotextile in agriculture.
7. Aquaculture:
Aquaculture are directed to sustainability of land and water resources to ensure harmony among the fish farming and the environment. Sustainable offshore net cage fishing systems are widely used all over the to reduce over pumping of underground water in areas near the coastline. Geotextile purse nets for offshore and pelagic fisheries are commonly used in many counties. Geotextile applications for the fishing industry will improve in the near future.
8. Commercial development:
The sustainable applications of geotextiles has continued to increase cause for cost savings realized by owners, developers, and contractors over the past 40 years. The traditional materials are replaced. Cause geotextiles provide as much as 50% cost savings. Combined with ease of installation and low labor costs in installing geotextiles have led to significant growth in the commercial development market over the past several decades.
Conclusion:
Textiles are not only clothing that protects our body but also protects our motherland. Extensive awareness might be created about sustainable applications of geotextiles in civil engineering. It is very important for sustainability, all geotextiles be composed of strong, durable, chemically inert polymeric materials that are resistant to the effects of ground conditions, weather, and aging.
Geotextile are eco-friendly to modern sustainable requirements of environment. Carbon foot-printing techniques are used to establish sustainable geotextile for a solution over set life cycle boundaries.
The Agro-based geotextiles (woven textiles based on cotton, jute, coir) are also growing sector. It has the advantage of sustainable bio-degradable cost effective. In future sustainable applications of geotextiles in civil engineering will make world more suitable for mankind. To explore this potentiality of sustainable applications of geotextiles we have to more researches are needed in this field
References:
- Geotextile From the Design to Application by R.M. Koerner
- Geotextile: It’s Application to Civil Engineeering – Overview by Dr. Bipin J Agrawal
- https://textilelearner.net/different-important-functions-of-geotextile/
- https://www.technicaltextile.net/articles/engineering-use-of-textiles-in-geotextile-6726
Author of this Article:
Md Mahedi Hasan
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali.
Email: mh18.bd@gmail.com
