What is Technical Textile?
Textiles are divided into clothing, household fabrics, and technical textiles. Clothing and household fabrics (curtains, textile wallpaper, upholstery fabrics, carpet, and floor coverings) seem to be easily defined. It could therefore be concluded that all other textile products constitute the group of technical textiles. All textile products that are designed for the most part to conform to their functionality are technical textiles. In other words, technical textiles can be defined as the textiles in which the performance properties are of greater importance than the aesthetics.
Technical textile products are designed for their functional property rather than their aesthetic properties. Technical textile materials are designed to have high level of physical, mechanical, thermal and/or chemical properties for use in specific applications within industrial sectors such as earthworks, construction, civil engineering, transport, defense, medical and healthcare. Sometimes other terms like industrial textiles, functional textiles, engineered textiles, performance textiles, etc. can be used instead of technical textiles.
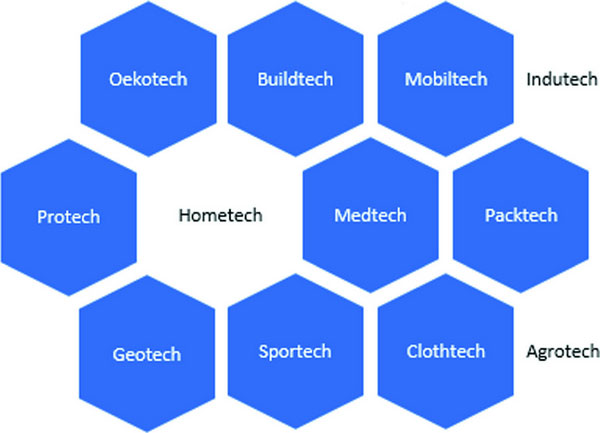
Classification of Technical Textiles and Their Applications:
Classification of the technical textile products is based on the area of application. For example, products related to the medical and health care are a part of Medtech which stands for medical textiles. There are different types / branches / categories of technical textiles. Here top 12 branches of technical textiles are given below:
- Aggrotech or Agro Textile
- Buildtech
- Clothtech
- Geotech or Geotextiles
- Hometech or Home Textiles
- Indotech or Industrial Textiles
- Medical Textiles
- Mobiltech / Automobiles
- Oekotech
- Packtech or Packaging Textile
- Protech or Protective Textile
- Sportech / Sports Textiles
Above types of technical textiles are briefly described below:
1. Aggrotech or Agro Textiles:
The textiles used in agriculture are called as agro textiles. It deals with the technical textile products used in the agriculture, horticulture, forestry, farming and fishing industries. Depending upon the applications, the raw materials for aggrotech products must have these properties.
- Resistance to sunlight and weather (frost, wind, rain, hail storm, etc.)
- Resistance to microorganisms
- Long service life and lightweight
- Biodegradability
Both natural and synthetic fibers are used for aggrotech products. Some of the commonly used natural fibers for aggrotech products are jute, flax, ramie, etc. These fibers are used for their biodegradable property. Similarly, polypropylene (PP), polyethylene, nylon, and polyester, are also used for their good ultraviolet (UV) resistance, good strength and long service life properties. Weaving, knitting and non-woven technologies are used to manufacture aggrotech products. Some of the examples of aggrotech products are sunscreens, bird protection nets, plant nets, harvesting nets and packing material for agriculture products.
2. Buildtech:
The textiles that are used in the construction and architectural application are termed as buildtech. This sector consists of technical textiles that are used in the construction of temporary buildings, permanent buildings and structures. These are widely used for roofing, insulation and cladding, acoustic and structural purposes. A major growth in this sector is due to the demand for eco-friendly, lighter and high-performing and sustainable materials and products.
You may also like: Application of Textiles in Building and Construction
One of the advantages of using textiles in buildings consists of providing a large obstruction-free span, ease of deconstructing and re-erecting as per the requirements. Depending on the architecture requirements, fabrics can be made into different shapes and appearances. Similarly, fiber-reinforced composites can be made from aramid, glass or carbon fibers to create structures with excellent strength to weight capability, high stiffness to weight and have design flexibility.
Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- High tensile and high tear strengths
- Resistant to deformation
- Resistant to extension under tension
- Resistant to wind and water
- Resistant to degradation, especially with exposure to sunlight
- Low-maintenance fabrics
- Acoustic insulation and thermal balancing functions
Carbon, nomex, wool, polyester, nylon, PP and glass fibers are widely used in buildtech applications. Weaving, knitting, braiding, non-woven and composite technologies are used to manufacture buildtech products. Sometimes, fabrics are coated with special finishes in order to have waterproof functions. For example, polyester fabrics are usually coated or laminated with polyvinyl chloride or polyvinylidene chloride films. Some of the examples are insulation, acoustic products, architectural fabrics, glass fiber reinforced concrete, etc.
3. Clothtech or Clothing Textiles:
Clothtech includes fibers, yarns and textiles used as technical components in the manufacturing of clothing such as sewing threads, interlinings, waddings and insulation. Clothing textiles forms a part of the technical components of clothing and footwear sectors. Some of the products are interlinings, zip fasteners, elastic narrow fabrics velcro, shoe laces, umbrella cloth, sewing threads, etc.
Some of the material requirements are as follows:
- Good tensile and high tear strengths
- Resistant to deformation
- Good elasticity
- Resistant to extension under tension
- Good dimension stability
- Good abrasion resistance
- Good seam strength
Spinning, weaving, knitting, braiding and non-woven technologies are used to manufacture clothtech products. Viscose, polyester, nylon and PP are used for clothtech products.
4. Geotech or Geotextiles:
All the fabrics (woven, nonwoven and knitted textile materials) which can provide a range of primary functions such as support, drainage and separation at or below ground level, lie in the category of geotextiles. Geotextiles are a part of geotech products. Geotextiles are continuous sheets of woven, non-woven, knitted or stitch-bonded fibers or yarns. The sheets are flexible and permeable and generally have the appearance of a fabric. Geotextiles are used for separation, filtration, drainage, reinforcement and erosion control applications. Furthermore, geotextiles form a part of geosynthetic family.
You may also like: Geogrid: Types, Structures, Installation and Application
Since geotextiles are permeable textile materials, they are utilized with foundation soil, rock, earth and geotechnical engineering material for a particular structure of system. The textile material increases soil stability and decreases water erosion and helps with drainage, thus improving soil characteristics. These materials are constructed into fabrics like mats, webs, nets, grids and plastic sheets.
Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- Permeable
- High strength and modulus
- Maintain rigidity and stability to withstand strain, stress, tension and forces
- Resistant to rupturing and puncturing
- Flexible
- High abrasion resistance
- Resistant to contaminated ground water
- Resistant to fungal attack and rotting
- Resistant to UV radiation
- Biodegradable
- Good durability
Geotextiles can be woven, knitted or non-woven and also be made of natural or synthetic fibers. Polyester, polyamide, polyethylene, PP, flax, hemp, kenaf and jute fibers are used for geotech products.
5. Hometech or Home Textiles:
It deals with the technical textile components used in the furniture, household textiles and floor covering applications. Some of the examples of these products are carpet backing layers, mattress components, blinds, stuff toys, furniture fabrics, etc.
Some of the material requirements are as follows:
- High strength and modulus
- Good durability
- Flexibility and good elastic recovery
- Compression and recovery
- High abrasion resistance
- Good handle and drape
Home textiles can be made from woven, knitted, braided or non-woven processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of hometech products. Acrylic, viscose, wool, polyester, PP, nylon and jute fibers are commonly used for hometech products.
6. Indutech or Industrial Textiles:
Indutech includes technical textile products used in the manufacturing sector. It deals with the products used in filtration, conveying, cleaning and other industrial applications. Some of the examples of indutech products are filters, conveyor belts, ropes and cordages, abrasives products, etc. Filtration is a process of separating solid particles from liquids and gases by passing them through the filter media. Filtration is divided into two major categories: dry filtration for air, gas and particle and wet filtration for liquids. Air filtration plays an important role in improving air quality and cleaner environment. Water filtration is one of the ways of improving water quality and safety.
Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- High strength and modulus
- Good durability
- Flexibility and good elastic recovery
- Good thermal and chemical resistances
- High filtration efficiency and low pressure drop
- Good dimensional stability
- Good bursting strength
- Good abrasion resistance
- Resistant to UV radiation
Indutech products can be made from woven or non-woven processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of indutech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for indutech products are PAN, PPS, carbon, high-density polyethylene (HDPE), glass, polyester, PP, nylon, etc.
7. Medical Textiles:
Textile materials developed and used in medical and hygiene applications fall under medtech sector. Medical textiles can be considered as a part of the wider group of technical textiles. Growth in the medtech sector is mainly due to increasing innovation in medical and textile fields and increasing demand for newer materials with better functionality. Medtech products are divided into four different areas: non-implantable textile materials, implantable textile materials, extracorporeal devices, and healthcare and hygiene products. Some of the example of these products are bandages, absorbent gauges, vascular grafts, heart valves, artificial kidney, liver, surgical gowns, caps, gloves, masks, aprons, personal protective equipment etc.
Some of the advantages of medtech products are as follows:
- Prevention of hospital infections and cross infections
- Breathability functions
- Higher comfort level, e.g., for surgical gowns
- Engineered to have high barrier to blood and other body fluids
- Compatibility with various types of sterilization techniques
- Cost-effective
The material requirements for medtech products are as follows:
- Biocompatible and sterile
- Anti-allergenic and antibacterial
- Good resistance to alkalis, acids and microorganisms
- Good dimensional stability and elasticity
- Good strength and durability
- Free from contamination or impurities
- Absorption/repellency and air permeability
Medtech products can be made from spinning, weaving, knitting, braiding and nonwoven processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of medtech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for medtech products are cotton, viscose, silk, spider silk, polyester, PP, spandex, PLA, etc.
8. Mobiltech / Automobiles:
Transportation textiles or mobiltech can be defined as a technical textile material that has been developed for manufacturing all types of transportation, such as all road vehicles, trains, marine vehicles and aeroplanes. Mobiltech products for the automotive industry can be broadly classified into two categories, viz. visible and concealed components. Visible components include seat upholstery, carpets, seat belts, headliners, etc. Concealed components include noise vibration and harness components, tyre cords, composite reinforcements for automotive bodies, rail bodies and components, aircraft bodies, wings, engine components, boat and yacht components, bodies etc. There is a variety of functions that each transportation textile can provide. It includes comfort and style for the user, protection against impact, protection against UV rays, weight-saving factors in the aircraft sector, etc..
- Resistance to sunlight and UV radiation
- Resistance to abrasion
- Good strength and modulus,
- Good dimensional stability
- Reduced flammability and heat stability
- Resistant to mildew
- Ease to clean
Mobiltech products can be made from weaving, knitting, non-woven, coated, laminated or other composite processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of mobiltech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for mobiltech products are acrylic, nylon, polyester, PP, polyethylene, aramid, carbon, glass, wool, hemp, flax, kenaf, sisal, etc.

9. Oekotech:
Any textile product which is produced in eco-friendly way and also processed under eco-friendly limits come under oekotech. Oekotech deals with the technical textiles products used for environmental protection. Oekotech application segment includes concepts in environmental protection, waste disposal and recycling processes. It refers to the use of geosynthetic products to secure landfills against leakage of municipal or hazardous waste.
Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- Permeable
- High strength and modulus
- Good dimension stability
- Good abrasion resistance
- Resistant to fungal attack and rotting
- Resistant to UV radiation
- Good durability
Oekotech products can be made from weaving, knitting and non-woven processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of oekotech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for oekotech products are acrylic, nylon, polyester, PP, polyethylene, jute, hemp, flax, kenaf, etc.
10. Packtech or Packaging Textile:
Packtech deals with the technical textiles products used for packaging applications. Packtech products include the following: polyolefin woven sacks, flexible intermediate bulk container, leno bags, jute hessian sacks, tea bags (filter paper), soft luggage, absorbent meat pad, etc.
Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- High strength and modulus
- Good dimension stability
- Good abrasion resistance
- Resistant to fungal attack and rotting
- Resistant to UV radiation
- Good durability
- Good flexibility
Packtech products can be made from spinning, weaving, knitting and non-woven processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of packtech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for packtech products are nylon, polyester, PP, polyethylene, HDPE, low-density polyethylene (LDPE), jute, etc.
11. Protech or Protective Textiles:
Protech can be defined as technical textile materials, apparel and equipment that are used for protecting personnel and equipment from various environmental and industrial hazards. The variety of protective functions that needs to be provided by different textile products is considerable and diverse. It includes protection against cuts, abrasion, ballistic and other types of severe impact including stab wounds and explosions, fire and extreme heat, hazardous dust and particles, nuclear, biological and chemical hazards, high voltages and static electricity, foul weather, extreme cold and poor visibility.

You may also like: Application of Textile Materials for Protective Textile
Some of the material requirements are as follows:
- High strength and modulus
- Good dimension stability
- Good durability and flexibility
- Permeable and breathable
- Lightweight and low bulk
- Good handle and drape
- Water repellent and waterproof
- Windproof and snow shedding
- Heat and flame resistant
- Good impact and shock resistant
Protech products can be made from weaving, knitting, non-woven, coated, laminated or composite processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of protech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for protech products are acrylic, nylon, polyester, PP, polyethylene, aramid, PAN, carbon, glass, polybenzimidazole, DyneemaR, Kevlar, SpectraR, ultra-high modulus polyethylene, spandex, flame-resistant cotton/polyester/viscose, wool, cotton, hemp, linen, etc.
12. Sportech / Sports Textiles:
Sportech deals with technical textile products used for sports purposes. Some of the sports textiles products are artificial turf, high-performance swimwear and sportswear, parachute fabrics, sail cloth, sport shoe components, sport composites, etc.

Some of the materials requirements are as follows:
- High strength and modulus
- Good dimension stability
- Good durability and flexibility
- Permeable and breathable
- Quick drying
- Good elasticity
- Water repellent and windproof
Sportech products can be made from weaving, knitting and braiding processes. Both natural and synthetic fibers are used in the manufacturing of sportech products. Some of the commonly used fibers for sportech products are nylon, polyester, PP, polyethylene, LDPE, spandex, wool, etc.
References:
- Fibres to Smart Textiles: Advances in Manufacturing, Technologies, and Applications Edited by Asis Patnaik and Sweta Patnaik
- Textile Engineering – An Introduction Edited by Yasir Nawab
- Fibres to Fabrics by Bev Ashford
- Textile Technology: An Introduction, Second Edition by Thomas Gries, Dieter Veit, and Burkhard Wulfhorst
- Fibers for Technical Textiles, Editors Sheraz Ahmad, Abher Rasheed, Yasir Nawab
Author of this article:
Abrar Ahmed
Dept. of Textile Engineering
BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology
Email: abrara1999@gmail.com
You may also like:
- Geotextiles: Types, Properties, Functions, Applications & Market
- Clothing Textiles: A Branch of Technical Textiles
- Aerospace Textiles: Applications of Textiles in Space Technology
- Home Textiles in Bangladesh: Applications, Global Market Share and Opportunities
- Sports Textiles: Applications, Functional Properties and Opportunities
- Conductive Textiles: Types, Properties and Applications
- Application of Smart Textiles in Medical and Healthcare
- Application of Textiles in Building and Construction
- Application of Phase Change Materials in Smart Textile
- Smart Textile Revolution: Towards a Smart Future
