Imagine a number “10000000000”. Can you imagine it? If you can, just remember it, I will tell you about it later. Around 20% of wastewater is produced by fashion industry. 20,000 litters of water are needed for 1kg of cotton production[1]. Textile industry is one of the top 3 water wasting industry in China[1]. 5,000 gallons of water is needed just to make a t-shirt and pair of jeans[1]. The average amount of textile thrown by an average person is around 37kgs[2]. Only 3% arable land of the world is used for cotton production, but it is responsible for 11% of pesticides and 24% of insecticides[1]. One trillion kilowatt-hours are used yearly by global textile industry which is equal to 10% of the global total carbon impact[2]. All these things show us the importance of “Textile Recycling”.

What is textile recycling?
In simple word textile recycling is recovering yarn, fibre, fabric etc and reprocess them to make new useful product depending on their composition, condition and most important resale value[3].
Importance of textile recycling:
Textile industry is trillion-dollar business globally[8] and it is not surprising that a trillion-dollar industry produce million tonnes waste.
Environmental Importance:
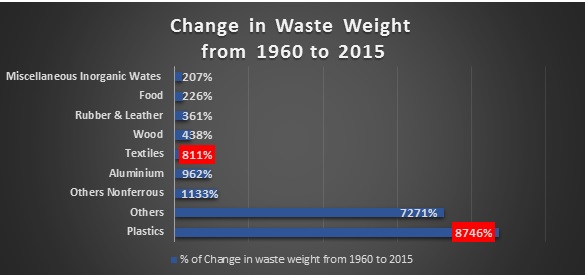
- According to EPA data textile waste increased 811% since 1960 to 2015. In 2016 2.01 billion tons of solid waste produced and 17 million tons were textile waste.[5]

- It can reduce green house gases. Because when people throw clothing in landfill, those cloth lack in oxygen for their break down. When they don’t get it, they produce by-products like methane.[4]
- By using recycle cotton we can save 20,000 litters of water on per kg cotton.
- By this fibre will get locally available and we don’t have to transport them from abroad. Because of that pollution will reduce and energy will be saved.[6]
- Manufacturing process is easy and quick that will save lot of energy.[5]
- Manufacturing process is eco-friendlier because raw materials are already dyed. So, in processing it needs zero dye, zero chemical and almost zero water.[5]
- Pressure on fresh resource will reduce.[6]
- Amount of plastic garbage will reduce as around 50% of PET bottles in Europe are used for producing fibre.[5]
Economic Importance:
- CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of Global textile recycling market is around 19% during 2014-19.it is expected to go $0.8 billion at a compound annual growth rate of 5.2% by 2026 according to report of Allied market research.[5]
- It reduces demand of textile chemicals such as dye, fixing agent etc.[6]
- By textile recycling up to 95% of textile waste can be recycled which goes to landfill.[2]
- Lesser energy, dye, chemical required that means reduce in process cost.
- Waste will be used as raw material so no cost for buying raw materials.[5]
- Manufacture cost of recycle yarn and their products is less then manufacturing cost of virgin yarn and their products.[5]
- We can save landfill space. These landfills are harmful for environment. It will also reduce municipal budget and the health of entire community.[4]
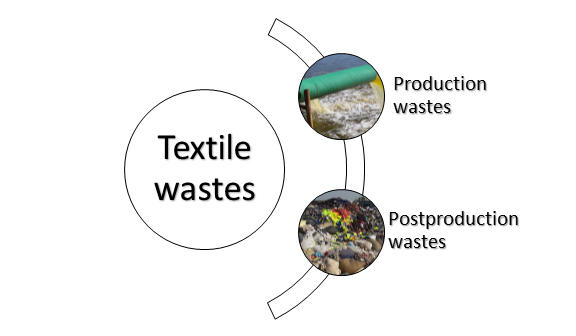
Sources of textile waste for recycling process:
Most of the material comes for textile recycling can be divided into two groups:
- Pre-consumer or post-industrial waste: These materials are by-product created from garment, yarn and fabric manufacture. Example a factory cuts pattern for clothing out of big sheets of fabric. As a result, it has lot of in-between pieces to discard and it is called post-industrial cotton waste.
- Post-consumer waste: It includes vehicle solitary, household item, garments and other items.
Recycling that are done in textile:
- Wool recycling.
- Used footwear recycling.
- Cotton recycling.
- Other textile waste recycling.
- Used cloth recycling.
- Carpet recycling.
- Used and recycled bag.
- Rags and wipers.
- Polyurethane foam recycling.
- Nylon and nylon fibre recycling.
- Other synthetic fibre recycling.
- Recycling of polyester and PET bottles. etc.
Textile recycling methods:
Textile industry is one of the most polluting industries in the world because not only its production but also its consumption produces waste. Worldwide around 80 billion garments are produced every year[8].
- Physical or mechanical method: This method is widely used in recycling industry for simpler, cheaper and eco-friendly process. In this process manufacturing and post-consumer products are reprocessed into new products by reclamations process or commingled plastic process.
- Chemical recycling: Unlike physical recycling process chemical process produce high quality fibres that is almost similar to the virgin fibres. So that no new fibres are needed to support the chemical process. But this process is not widely used as physical method. It converts high molecular weight polymers into low molecular weight substance. It is done by the chemicals that facilitate methanolysis, glycolysis, hydrolysis etc[3].
Textile recycling technologies:
- Thermal recycling technologies: Its aim is to recover heat energy generated from the incineration of fibre wastes as electrical or thermal energy. Transforming polyethylene terephthalate into fibre is the most widely used and eco-friendly way[7].
- Chemical recycling technologies: In this way monomers are recovered from waste fibre by poly decomposition. From recovered monomers impurities can easily be removed[7].
Product made from recycled textile: Companies like Patagonia, H&M, Lindex etc sell sustainable cloth. In Finland, pure waste is a clothing company make t-shirt from recycled fibre in their 95% wind powered factories[3]. In Sweden company like Lindex and H&M use post and pre-consumer waste fibre within their new cloth lines[3].
Conclusion:
So, you are going to throw your pants and t-shirt in landfill. Why don’t you think about it again? Remember that number at the beginning of the article. That number represent “10 million tonnes” or “10 billion kilo grams” of clothing waste[2]. It is the amount of clothing goes into landfill every year only in “North America”[2]. Now push your imagination and think about the world.
References:
- https://edgexpo.com/fashion-industry-waste-statistics/
- https://wrwcanada.com/en/get-involved/resources/textiles-themed-resources/textiles-waste-facts
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Textile_recycling
- https://www.gogreendrop.com/blog/7-important-reasons-to-recycle-your-clothes/
- http://textilefocus.com/10919-2/
- https://textilelearner.blogspot.com/2012/02/textile-recycling-importance-of-textile.html
- https://www.textiletoday.com.bd/recycling-textile-wastes/
- https://www.thebalancesmb.com/the-basics-of-recycling-clothing-and-other-textiles-2877780
- Recycling in Textiles Edited by Youjiang Wang
- Textiles and Clothing Sustainability: Recycled and Upcycled Textiles and Fashion Edited by Subramanian Senthilkannan Muthu
Author of this Article:
Md. Sadman Nafe
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali.
Email: nafe2290@gmail.com